* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANSWERS Cell Unit Study Guide 2013
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
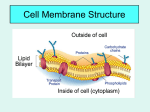
Cell Structure and Transport Study Guide Cell Theory 1. Who was the first scientist to observe dead cork cells under the microscope and name them cells? Hooke 2. State the three parts of the cell theory: a. All living things are made of cells b. Cells are the basic unit of life c. Cells come from other cells d. All cells contain DNA Cells: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic 3. Circle the correct word: A eukaryotic/ prokaryotic cell is one that has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. 4. List one example of a prokaryotic cell: Bacteria 5. List two examples of eukaryotic cells: Plant and Animal Prokaryotic Cells 6. Draw a bacterial cell (prokaryote) and label the DNA, cell membrane and cell wall. Eukaryotic Cells: Plant vs. Animal Cells, Organelles cell membrane cell wall (plant cell only) chloroplast (plant cell only) cytoplasm vacuole Cell Membrane Lysosome Nucleus Nucleolus lysosome (animal only) mitochondria ER Golgi apparatus Nucleus Centriole Cell Wall Cytoplasm Rough ER Central Vacuole Smooth ER Nuclear Mem. Ribosomes Vacuole Golgi Body Chloroplast Nucleolus Nuclear envelope (membrane) Ribosomes (on ER and in cytoplasm) 8. What three organelles are found in plant cells but not in animal cells? Cell wall, chloroplast, and large vacuole 9. What organelle is found in animal cells but not in a plant cells? Centrioles and lysosomes 10. Complete the organelle function chart: Organelle Function (Job) Mitochondria Gives energy to cell (like a battery) Nucleus Brain of the cell; protects DNA Ribosomes Make proteins Lysosomes Get rid of waste (garbage men) Cell membrane Protects the cell and gives shape; Lets certain things in and out Transports things around the cell (like a road) Packages and receives things to send in the cell (like UPS) E.R. Golgi bodies/complex/apparatus Cell Membrane 11. What is meant by “The Fluid Mosaic Model?” That all the parts of the cell membrane (phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol) can move around in the membrane. 12. Is the cell membrane selectively permeable (semipermeable), or can anything move in and out of the cell? Yes, only certain things can move in and out Solutions: Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic 13. Draw a cell in a hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solution. Hypotonic Label with arrows the movement of water. Isotonic 14. If you put an Elodea plant cell in salt water, what would the cells look like? SHRINK (salt water is hypertonic) Hypertonic The cells would 15. If you put an Elodea plant cell in fresh water, what would the cells look like? The cells would get BIGGER (water is hypotonic) 16. Is the salt water solution hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic? Hypertonic 17. What would a red blood cell (animal cell) look like in salt water? Shrink 18. What happens when you put a red blood cell in 100% water? Get bigger Cell Transport 19. Circle the correct word: Passive Transport does/does not require energy. 20. Describe the three types of passive transport: a. diffusion: any molecule moves from high to low concentration b. osmosis: water moves from high to low concentration c. facilitated transport: proteins help molecules diffuse through a membrane 21. When does diffusion stop? (When it reaches ____________________) Equilibrium 22. Circle the correct word: Active transport does/does not require ATP (energy). 23. Describe the following examples of active transport: a. Protein pump: Proteins open and close to let things cross the membrane using energy b. Endocytosis: Molecules move into cells using energy c. Exocytosis: Molecules move out of cells using energy 24. Which molecule in the cell membrane moves Na and K into and out of a cell? Does this require ATP energy? Protein pump; YES active transport always uses energy Microscope 25. How do you carry a microscope? Holding the arm and the base (top and bottom) 26. How do you calculate the total magnification of a specimen? Multiply the objective you are using times the eyepiece (10 x the objective being used) 27. Name the objective lens and focus knob that you would use when you first look at a specimen under the Microscope. Low objective (red) and coarse adjustment (big knob) 28. While looking into a microscope, what direction would a letter “e” move if you move the slide to the right? Left 29. While looking into a microscope, what direction would a letter “e” move if you move the slide to the left? Right