* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL ORGANELLES – VOCABULARY REFERENCE SHEET
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
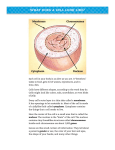
CELL ORGANELLES – VOCABULARY REFERENCE SHEET VOCABULARY WORD CELL TYPE & LOCATION ORGANELLE CELL MEMBRANE CELL WALL CENTRIOLE CHLOROPLAST FUNCTION (JOB) A specialized structure within the cell that carries out a specific job to help the cell function. A double layered skin that acts as a barrier to enclose the contents of the cell, give it All Cells support, and control the substances that enter and leave the cell. (outer layer surrounding the cell) All Cells A strong, rigid layer of nonliving material that covers the outside of some cell types Bacteria & Plant Cells and provides protection, structure, and maintains pressure for the organism. (outside of the cell membrane of some cells.) Eukaryotic (near the cell nucleus in the cytoplasm) A small set of tubes fused together that help in pulling the cell apart during mitosis (cell division). They create the spindle fibers that actually pull the cell apart. Plants, some protists & some A double layered compartment that captures light energy in green chlorophyll and uses the light energy, water, and carbon dioxide to create glucose (sugar) for the cell. bacteria. (found within the cytoplasm) CHROMATIN / CHROMOSOMES Eukaryotic (within the nucleus) An X-like structure made up of proteins and coiled up DNA that carry the genetic information from the parent to the offspring. CYTOPLASM All Cells (fills up inside of cell) A gel-like substance that fills the entire inside of the cell, except for the nucleus. It holds the organelles in place and allows for transport of substances. All Cells (Eukaryotes - nucleus) (Prokaryotes - cytoplasm) A double-stranded helix that is made up of nucleic acids that code for specific traits, activities, and the production of proteins in the cell. DNA A stack of membrane bound vessels that take protein molecules and combine them to make more complex protein molecules. It then packages them for use within the cell or to be shipped out of the cell. (near the ER in cytoplasm) Eukaryotic GOLGI APPARATUS / GOLGI BODY Eukaryotic A network of tube-like passageways that create and transport proteins to different places within the cell. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (outside of the nucleus) LYSOSOME Eukaryotic (within the cytoplasm and near vacuoles) A round membrane-bound sac that hold enzymes that are used to break down waste materials and cellular debris. All Cells (within the cytoplasm) Rod-like membrane bound organelle that takes in sugar and releases its stored energy in a process call cellular respiration. MITOCHONDRIA A non-membrane bound structure within the nucleus that is primarily responsible for Eukaryotic the production of ribosomes. (found within the nucleus) NUCLEOLUS A membrane-enclosed structure in the cell that safely stores the cell’s DNA and Eukaryotic determines which genes are active and controlling the activities in the cell. (in the cytoplasm) NUCLEUS A double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm and Eukaryotic NUCLEAR MEMBRANE/ controls the substances that enter and leave the nucleus. NUCLEAR ENVELOPE (surrounding the nucleus) PROTEINS All Cells (make up the organelles and cell) Chains of amino acids that make up and carry out all processes in a cell and living organisms. They may be enzymes, build the structure of a cell or cell part, or send signals to repair the cell or fight off intruding organisms. RIBOSOMES All Cells (floating in cytoplasm and connected to the ER) A two-piece structure that reads the code of messenger RNA (a form of DNA) and assembles amino acids to create a specific protein. Most Cells (within the cytoplasm) A membrane-bound organelle that acts as a storage chamber for needed materials, waste products, and water (which helps plants maintain structure). VACUOLE