* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
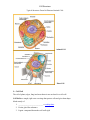
Cell Structure Typical Structures Found in Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Wall The cell of plants, algae, fungi and most bacteria are enclosed in a cell wall. Cell Walls are tough, rigid outer coverings that protect cells and give them shape. Made mostly of: 1. ____________________________ a carbohydrate. 2. Pectin- glue-like substance. 3. Lignin- compound that makes cell wall rigid. Cell Membrane-“A barrier with doorways” The protective layer surrounding every cell is the ____________ ____________. In plant cells: located just inside the cell wall. In animal cells: forms the outer covering of the cell. Functionprovides _______________________ control the movement of materials into and out of the cell Allows nutrients to move into the cell, while waste products leave. Cytoplasm Cells are filled with a gelatin-like substance called __________________________ Constantly flows inside the cell membrane. Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Throughout the cytoplasm is a framework called the cytoskeleton. Helps maintain its shape and enable some cells to _____________________ The cytoskeleton is made up of thin, hollow tubes of protein and thin, solid protein fibers Ribosomes: Protein Factories Manufacturing Proteins One substance that takes part in nearly every cell activity is ___________________ Part of cell membranes Needed for chemical reactions that take place in the cytoplasm. Cells make their own proteins on small structures called _______________________. Receive directions from the hereditary material on how, when, and in what order to make specific proteins. Float freely- Many attached to the endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes are considered organelles, but are not membrane-bound. Membrane-Bound Organelles Structures within the cell are called organelles, the largest is the __________________. Nucleus- Control Center of Cell •Directs all cellular activities •Contains long, threadlike, hereditary materials made of DNA. •DNA is the chemical that contains the code for cell’s structure and activities. •nucleolus also is found in the nucleus, and is where most ribosomes are made. Chloroplasts- Energy Producers In plant cells, food is made in green organelles in the cytoplasm called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Captures the energy of sunlight which can be used to produce food for the cell. Mitochondria-The __________________________of the Cell •Rod shaped structures that supply most of the energy for the cell. •Releases energy by breaking down food into carbon dioxide and water. Endoplasmic reticulum- Transportation System of the Cell •A series of clear tubular _____________________________ •Carries proteins from one end of the cell to the other. •Lead out from the nucleus. •Some lead to the cell membrane, others to all other areas of the cell. The ER may be “rough” or ______________________ 1. Rough ER •Ribosomes are attached to areas on the rough ER. •Makes proteins that are moved out of the cell or used within the cell. 2. Smooth ER •Processes cellular substances such as lipids that store energy. Golgi bodies “Packaging Center” •Stacked, flattened membranes. •After proteins are made in a cell, they are transferred to the Golgi bodies. •The Golgi bodies ________________proteins and other cellular substances and _________________________ them. Vacuoles Storage Tanks for Cells •Membrane-bound spaces used for the temporary _______________________. •Stores water, waste products, food, and other cellular materials. Lysosomes Clean up Crews for the Cell Contain digestive chemicals that help ___________________ __________________ 1. cell waste, 2. worn-out cell parts. 3. viruses and bacteria taken into a cell.