* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 6 - Ltcconline.net
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
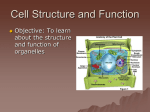
Principles of Biology - Biology 101 Lake Tahoe Community College Fall Quarter Instructor: Sue Kloss _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Ch. 6 - Introduction to Cells/Organelles, Structure, Movement ________________________________________________________________________________________ I. Introduction to cells 1. cytosol 2. cytoplasm 3. plasma membrane 4. chromosomes 5. ribosomes A. Cell size relates to function B. Natural limits on cell size 1. lower limit 2. upper limit 3. relationship of surface area to volume C. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) 1. Nucleoid region 2. Ribsomes 3. plasma membrane 4. Bacterial cell wall 5. Capsule 6. Pili 7. flagella D. Eukaryotic cells 1. cytoplasm 2. organelles 3. cellular metabolism 4. partitioning 5. Eukaryotic cells have about 10x the diameter of prokaryotes 6. Plant and Animal cell differences III. Eukaryotic cells - Organelles of the Endomembrane system A. Nucleus - genetic control center 1. chromatin 2. chromosomes 3. nuclear envelope 4. nucleolus 5. ribosomes 6. nuclear lamina B. Endomembrane system 1. many organelles work together in synthesis, storage and export of imp. molecules C. Endoplasmic reticulum 1. rough er 2. smooth er D. Golgi apparatus - close partner to ER 1. receives and modifies substances produced by ER 2. Golgi stacks have distinct polarity between membranes of cisterna (reservoirs) on opposite sides 3. substances sent to correct destination in transport vesicles E. Lysosomes (Gr. - breakdown body) 1. produced by ER and Golgi apparatus 2. consists of hydrolytic enzymes fuses w/ lysosome 3. (Fig.) digestive functions F. Vacuoles function in genl maintenance - central vacuoles in plant cells only IV. Organelles that convert energy – A. Chloroplasts 1. stroma 2. granum 3. inner and outer membrane 4. 3 compartments for chemical work B. mitochondria 1. ATP main currency of all work 2. 2 membranes 3. mitochondrial matrix 4. found in all eukaryotes 5. mitochondria move around and are active in cell C. peroxisomes 1. specialized metabolic compartment bounded by single membrane V. Cytoskeleton A. Microfilaments - solid helical rods of actin B. Intermediate filaments - varied group - fibrous proteins, ropelike structure C. Microtubules -straight hollow tubes composed of globular proteins VI. Cilia and flagella A. Cilia B. Flagella C. dynein walking VII. Extracellular components A. Cell walls of plants 1. much thicker than plasma membrane 2. cellulose 3. sticky polysaccharides glue cells together B. Extra cellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells 1. glycoproteins secreted by cells VIII. Cell Surfaces and Junctions A. plasmodesmata B. Cell junctions connect one cell to another in animal tissue 1. tight junctions 2. desmosome 3. gap junctions Homework Questions/Lesson Objectives for Chapter 6 - A Tour of the Cell _____________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 2. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. 3. Draw and describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the role of the pore complex. 4. Briefly explain how the nucleus controls protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. 5. Explain how the nucleolus contributes to protein synthesis. 6. Describe the structure and function of a eukaryotic ribosome. 7. Distinguish between free and bound ribosomes in terms of location and function. 8. List the components of the endomembrane system, and describe the structure and functions of each component. 9. Compare the structure and functions of smooth and rough ER. 10. Explain the significance of and draw the cis and trans sides of the Golgi apparatus and describe cisternal maturation model of Golgi function 11. Describe three examples of intracellular digestion by lysosomes. 12. Name three different kinds of vacuoles, giving the function of each kind. 13. Briefly describe the energy conversions carried out by mitochondria and chloroplasts. 14. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion and explain the importance of compartmentalization in mitochondrial function. 15. Identify the three functional compartments of a chloroplast. Explain the importance of compartmentalization in chloroplast function. 16. Describe the evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts are semiautonomous organelles. 17. Explain the roles of peroxisomes in eukaryotic cells. 18. Describe the functions of the cytoskeleton. 19. Describe and draw the basic structure of a plant cell wall. 20. Describe the structure and list three functions of the extracellular matrix in animal cells. 21. Explain how the extracellular matrix may act to integrate changes inside and outside the cell. 22. Name the intercellular junctions found in plant and animal cells and list the function of each type of junction.