* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recognise structures as seen under the electron microscope, e.g.
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
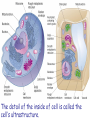
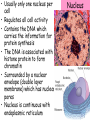
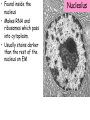
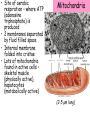
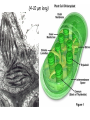
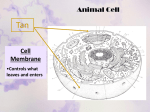
Lesson 2 • Recognise structures as seen under the electron microscope, e.g. nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, lysosomes and chloroplasts. • Outline the functions of these structures. The detail of the inside of cell is called the cell’s ultrastructure. • Usually only one nucleus per cell • Regulates all cell activity • Contains the DNA which carries the information for protein synthesis • The DNA is associated with histone protein to form chromatin • Surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double layer membrane) which has nuclear pores • Nucleus is continuous with endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus • Found inside the nucleus • Makes RNA and ribosomes which pass into cytoplasm. • Usually stains darker than the rest of the nucleus on EM Nucleolus Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum • Rough ER – with ribosomes – Protein synthesis • Smooth ER – without ribosomes – Synthesis of steroids and lipids • Intracellular membrane system – substances are transported in the spaces Golgi Apparatus • Stack of flattened sacs (cisternae), each separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane • Modifies and packages cell products (proteins from rER) • Encloses substances in vesicles to be secreted • Involved in production and secretion of many proteins, carbohydrates and glycoproteins • Vesicles containing digestive enzymes (hydrolytic enzymes) to break down materials • Surrounded by a single membrane. • White blood cell lysosomes break down microorganisms. • Lysosome (acrosome) in sperm cell helps to penetrate egg Lysosomes • Site of aerobic respiration – where ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced • 2 membranes separated by fluid filled space • Internal membrane folded into cristae • Lots of mitochondria found in active cells – skeletal muscle (physically active), hepatocytes (metabolically active) Mitochondria (2-5 µm long) • • • • • Chloroplasts Only found in plant cells – site of photosynthesis. 2 membranes separated by fluid filled space Inner membrane – flattened sacs called thylakoids. A stack of thylakoids is called a granum. Inside – stroma which is also involved in photosynthesis Chlorophyll molecules found on thylakoid membranes. (4-10 µm long) Ribosomes • Lots of ribosomes in a cell (50 000 or more) • Found on rough ER and also as free ribosomes in the cytoplasm • Site of protein synthesis (where mRNA and tRNA meet so the protein is assembled). Centrioles • Two short cylinders of microtubules • Pair found next to nucleus in animal cells • Aid cell division – move to opposite poles (ends) of the cell as spindle develops