* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Semester 1 Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
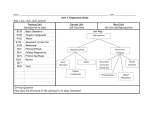
Biology Semester 1 Review (2012-2013) Unit 1 –Book Chapter 1 Characteristics of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Name and explain the characteristics shared by living things. How can each of the characteristics be observed and tested for? What are the 6 kingdoms of life? What characteristics define each kingdom? What are the parts of the light microscope? What is correct microscope technique? How is total magnification determined? How did we determine that the circles in the infected stool were living? Unit 2—Book Chapter 4 Cells 1. Summarize the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 2. Describe (BOTH ANATOMY AND FUNCTION) the organelles that are found in a eukaryotic cell. (nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, cilia, flagella, centrioles, plasma membrane, cell wall (in plant cells), central vacuole (in plant cells), chloroplasts (in plant cells). 3. Describe the differences between an animal cell, plant cell, and bacteria cell. 4. How did we determine that the mystery circles were a bacteria? Unit 3 Energy -- BookChapter 7 Cellular Respiration 1. Compare and contrast autotrophs and heterotrophs. 2. Describe two types of autotrophs. 3. Write the chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration discuss all reactants and products—specifically describe where each atom in each reactant ends up as a product. 4. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration: energy production, processes involved, similarities, differences, etc. 5. In what organelle does the Krebs cycle and the ETC take place? 6. How many ATP are produced in glycolysis? In the Krebs cycle? In the Electron transport chain? 7. Is cellular respiration more or less efficient than anaerobic respiration? What does this mean? 8. How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related to one another? --Book Chapter 6 Photosynthesis 1. Write the equation for photosynthesis. Discuss the origins of all reactants and products and the role of each. 2. In what organelle does photosynthesis take place? 3. Explain why both autotrophs and heterotrophs depend on photosynthesis to obtain the energy they need for life processes. 4. Describe the role of chlorophylls in the pathways of photosynthesis. 5. What gas is given off when water is split? 6. Describe what happens in the light dependent reaction and the light independent (dark) reaction 7. Be familiar with the leaf cross section diagram and how each of the parts relate to the process of photosynthesis. 8. How do gases get into and out of the leaf? How does water availability affect these processes? 9. Why do plants need to do both PS and CR? 10. Why is the sun considered the ultimate source of energy for all life forms on Earth? 11. Describe a test that would help to determine what type of feeder Cryptococcus gatti is. 12. How does the chemical BTB relate to PS and CR? 13. What tests did we do to try to determine the energy production and use in the Cholera cells? Unit 4 -- Book Chapter 5 Cell Transport 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the difference between passive and active transport? What is diffusion? Is osmosis the same thing as diffusion? Explain. Name and describe 3 types of passive transport. What role do transport proteins play in facilitated diffusion? What role do transport proteins play in active transport? If the concentration of solute molecules outside a cell is lower than the concentration in the cytoplasm, is the external solution hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic to the cytoplasm? What will happen to the cell in each situation? 8. Name and describe/explain 3 types of active transport. 9. Describe homeostasis of oxygen, carbon dioxide, ATP, and blood glucose. 10. Explain how homeostasis in the large intestines is affected by Cholera. Unit 5—Book Chapter 3 Biochemistry 1. How do carbon’s bonding properties contribute to the existence of a wide variety of biological molecules? 2. Compare the structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. 3. Name 3 monosaccharides. 4. Name 3 disaccharides and the monosaccharides that make them up. 5. Name 4 polysaccharides, where they are found, and the function of each 6. What are monosaccharides used for in living things? 7. Proteins are made of amino acids. Draw an amino acid and label the functional groups. 8. Draw 2 amino acids bonded by a peptide bond. 9. How do amino acids differ from one another? 10. Explain the functions of proteins. 11. Where are proteins found in living things? 12. Describe how the four types of lipids differ in structure from one another. 13. Why do phospholipids orient in a bilayer when in a watery environment, such as a cell? 14. . Explain the function of each type of lipids. 15. Where is each type of lipid found? 16. Compare and contrast condensation/dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. 17. What are put together in dehydration synthesis reactions to make complex carbs? Triglycerides? Proteins? Nucleic acids? 18. What substances should be given to Cholera patients to combat dehydration and provide quick energy. 19. Why is water not considered an organic molecule? Even though it is not why is important to living things? 20. Explain adhesion and cohesion and their importance.3 Chapter 8 Cell Reproduction -1. Why is mitosis considered an asexual process? 2. Explain the difference between cytokinesis in animal cells and cytokinesis in plant cells. 3. Diagram the cell cycle. 4. Diagram mitosis. 5. Describe all the instances you can think of in someone’s life when cell division occurs. 6. Discuss how cell division relates to cancer. 7. Why is mitosis important to the people from Bangledash infected with Cholera?