* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View document as pdf
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Acetylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
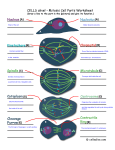
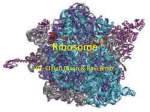
Ribosome Collection Lending Library: Ribosome Collection (RB) Teaching Points The synthesis of proteins relies on the activity of ribosomes, which are complexes of ribosomal RNA molecules and proteins organized into a large subunit and a small subunit. Together, these subunits form a functional ribosome, which catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids to produce a linear polypeptide chain, using the messenger RNA produced through transcription to determine the order of amino acids. With this collection, students can examine the interaction of the protein component and the ribosomal RNA component of the subunits. Students can also explore the differences between the large subunit (50s) and small subunit (30s) of the ribosome. The small ribosome subunit model displays the interaction of the three transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that are essential for the transportation of the amino acids into the ribosome complex in order for the peptide bond to form. Additionally, students can use the individual models of the tRNAs to further investigate the structure of these molecules. Models in this Collection • • • Large (50s) ribosome subunit Small (30s) ribosome subunit Three transfer RNA molecules Documentation Included • How do the models fit back in the suitcase? MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling Ribosome Collection| 1 General Model Information • • • • • The models are made of plaster with the ZCorp 3D printer. The models are shown in spacefill. The colors on the ribosome subunits represent recognized RNA domains, based on standard coloring schemes. The white portions of the ribosome subunits represent ribosomal proteins. Pipe cleaners approximate the path of mRNA and the newly synthesized protein. Model Details • • • Large (50s) ribosome subunit (PDB: 1ffk) Small (30s) ribosome subunit (PDB: 1giy) o Three tRNAs attached to small ribosomal unit are colored green Three transfer RNA molecules (PDB: 1ehz) o tRNA is colored in red and white to visualize the intrastrand base pairing o 3’ CCA which binds to amino acid is colored yellow o Anticodon is colored blue MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling Ribosome Collection| 2