* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Genes Work - Cochise College
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
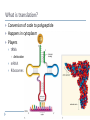
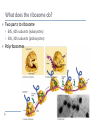
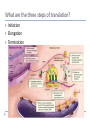
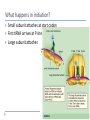
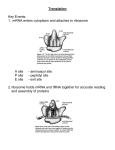
How Genes Work 14.1 Translation What is translation? Conversion of code to polypeptide Happens in cytoplasm Players tRNA Anticodon mRNA Ribosomes What does the ribosome do? Two parts to ribosome 60S, 40S subunits (eukaryotes) 50S, 30S subunits (prokaryotes) Polyribosomes What are the three steps of translation? Initiation Elongation Termination What happens in initiation? Small subunit attaches at start codon First tRNA arrives at P site Large subunit attaches What happens in elongation? Second tRNA arrives at A site P site tRNA transfers amino acids to A site Ribosome shifts to open A site “old” tRNA released at E site What happens in termination? Ribosome reaches stop codon Release factor attaches Subunits detach How Genes Work 14.2 Mutations What is a mutation? Permanent change in DNA sequence Can cause cancer Carcinogenesis Carcinogens vs. mutagens Two types of mutations Point Frameshift What is a point mutation? Substitution of wrong nucleotide What is a frameshift mutation? Original: Point mutation: THE BIG FLY HAD ONE RED EYE. THE BIT FLY HAD ONE RED EYE. Frame shift mutation: Addition: Deletion: THE BIT GFL YHA DON ERE DEY E. THE BIF LYH ADO NER EDE YE. Which is more dangerous?