* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell division - MrMcKennaBiologyPage
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
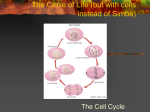
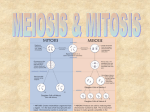
Cell division SQA questions What you should know ncreasing • Cell division is a means of i_________ the ells in an organism number of c____ ell a______, ctivities • Nucleus of the cell controls c___ ell ivision including c____ d_______ ach of the t___ wo cells produced by cell • E___ division has a complete set of hromosomes and the s_____ ame c__________ information. oss enetic This ensures there is no l____ of g______ nformation in the t___ wo new b____cells ody i________ two stages • Cell division occurs in ____ ytoplasm • Division of the c_________ and division of itosis the nucleus called m_______. • Before the nucleus divides each opied so there is a copy chromosome is c_____ hromatid ach of the chromosome (c_________) for e___ two new cells • The copy chromosomes are held together entromere by a c__________ and are called c__________ hromatids chromatids centromere original chromosome copy chromosomes 6 _______ 3 _____chromosomes in ach n___ ew c____ ell and e____ 3 chromosomes were in ___ copy chromosomes the original p________ arent (chromatids) b____cell ody 4 copy chromosomes _______ (chromatids) 2 _____chromosomes in ach n___ ew c____ ell and e____ ___ 2 chromosomes were in arent the original p________ ody cell b____ 6 copy chromosomes _______ (chromatids) _____chromosomes in 3 ew c____ e____ ach n___ ell and ___ 3 chromosomes were in arent the original p________ ody b______cell 8 copy chromosomes _______ (chromatids) 4 _____chromosomes in ach n___ ew c____ ell and e____ 4 chromosomes were in ___ arent the original p________ ody b_____cell What is the correct order? X W Y U V What is the correct order? U Y W V X What is the correct order? B D A E C What is the correct order? C B A D E 1 Describe what is happening Nuclear membrane disappears. Chromosomes being copied Draw or describe what happens next Copy chromosomes (chromatids ) appear What type of cell is this? Animal or plant Animal Describe what is happening Cytoplasm dividing by tucking in. Draw or describe what happens next Two cells are formed Describe what is happening 4 Copy chromosomes (chromatids) have formed Draw or describe what happens next Copy chromosomes (chromatids) line up at the equator of the spindle What type of cell is this? Animal or plant ? Plant Describe what is happening New cell wall forms between the two new cells Describe what is happening Copy chromosomes (chromatids) lined up at the equator of the spindle Draw or describe what happens next Spindle separates the copy chromosomes (chromatids) Describe what is happening The copy chromosomes (chromatids)are being separated Draw or describe what happens next New nuclear membranes form round copy chromosomes. New cell wall forms 4 mitosis Chromosomes (chromatids) are being pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell To make sure there is no loss of genetic information (genes) in the new cells mitosis New cell wall developing Division of cytoplasm Chromosomes becoming visible Nuclear membrane breaking down To make sure there is no loss of genetic information (genes) in the new cells