* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs and Teen Brain_12
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
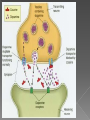
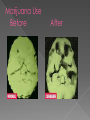
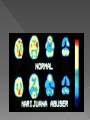
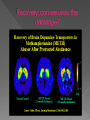
Remember, your brain grows until what age ____??? Also, the amygdala is _______________which makes your brain more sensitive to new, exciting, dangerous experiences Habit formation peaks now! Your Brain is STILL GROWING You have COMPLETE control over your decisions Alcohol and Drugs do impact: › your brain growth › Memory › Learning › Judgment › Your life! Drugs affect 3 main areas of the brain: › 1. Brain stem (medulla oblongata) in charge of “4 B’s”: breathing, heart beat, body temp and blood pressure › 2. Limbic system (amygdala is in here) Links together brain structures that control emotions like pleasure and pain › 3. Prefrontal cortex Decision making center Brain is very complex with billions of neurons that control all we feel, think & do. Drugs are chemicals and work by interfering with the way the brain and neurotransmitters work › What we saw on the last slide Some drugs can change the brain temporarily, others change it permanently › Marijuana and heroin activate neurons because they mimic neurotransmitters and send abnormal messages to brain › Amphetamines and cocaine cause neurons to release excessive amounts of natural neurotransmitters or prevent transporters from recycling; causing exaggerated messages in the brain All drugs “hijack” the limbic system, causing unusually large amounts of neurotransmitters to flood the brain this is the “High” This is why drugs “feel good” to those that use Neurotransmitters that drugs hijack: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Endorphins: the feel good, warm fuzzy one Dopamine: pleasure, positive, motivation Theobromine: stimulant, energy Anandimide: cannabinoid, hallucinogenic Phenylthylamine: “love drug” 1. Tolerance 2. Physical Brain Changes 3. Addiction What’s so wrong with getting high? 1. TOLERANCE (know this term) › Over time, you need more and more of the drug to achieve the same high › Drugs then become necessary for the person to feel “normal” 2. Drug users have physical changes in their brain that are critical to judgment, decisionmaking, learning, memory, and behavior Marijuana Use Before After 3. Addiction is a brain disease where one has: › Uncontrollable › drug craving, seeking, & use › that continues despite negative consequences Because your brain is still growing, addiction can happen fast Addiction usually begins in the teen years Drugs disturb a person’s normal hierarchy of needs and desires Drugs will substitutes some basic needs It depends: › How long did they use? › What drug and how much of it? › Brain is a vital organ so repair and recovery of the addicted brain depends on targeted and effective treatments that must address the complexity of the disease. › Research continues to gain new insights into ways to optimize treatments to counteract addiction's powerful disruptive effects on brain and behavior What works best: prolonged abstinence, our brains can recover some of their former functioning, enabling people to regain control of their lives. However, relapsing to drug abuse is not only possible but likely Drug Identification Test http://www.bbc.co. uk/suffolk/content/i mage_galleries/drug _awareness_2007_ga llery.shtml National Institute of Health (NIH) (2010). Addiction. http://science.education.nih.gov/supplements/nih2/Addiction/guid e/essence.htm National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA) (2010). Drug Abuse and Addiction. http://drugabuse.gov/scienceofaddiction/addiction.html Markowski, M. (2010). Education in Human Development and Family Science at Penn State University and Texas Women’s University. 1. Neurons in the brain communicate with each other by: › › › 2. A. passing axons B. releasing chemicals C. instant messaging When do you something you enjoy, you ________ system is activated › › › A. limbic B. digestive C. nervous 3. When someone uses drugs repeatedly, their brain ________________ › A. becomes trained to crave the drug › B. Becomes smaller than before › C. is not changed 4. After a prolonged period of drug abuse, the brain _______________ › A. needs less drug to get the same effect › B. needs more drug to get the same effect › C. experiences increasing amounts of dopamine 5. The brain’s reward system is part of the ____________ › A. sensory cortex › B. limbic system › C. spinal cord 6. Brain cells or neurons turn electrical impulses into ___________› A. chemical signals › B. movement › C. axons 7. Drugs work in the brain because they have similar _____________ › A. electrical charges as brain cells › B. size and shape as natural brain chemicals 8. Drugs of abuse create intense feelings because they __________-. › A. depress the nervous system › B. cause a rise in dopamine in the limbic system 9. drug abusers develop “tolerance” for drugs, meaning they need ______________ › A. more drug to get same effect › B. less drug to get same effect