* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 Cells
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
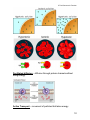
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
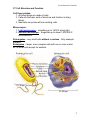
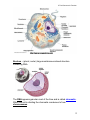
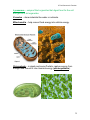
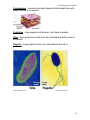
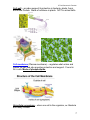
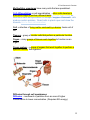
C7 Cell Structure & Function C7 Cell Structure and Function Cell theory states: 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Microscopes: 1. Light microscope – magnifies up to 1,500 X using light. 2. Electron microscope – magnifies up to about 1,500,000 X uses electrons Prokaryotes – very small cells without a nucleus. Only example: bacteria. Eukaryotes – larger, more complex cells with one or more nuclei. ex. all other cells except for bacteria. 1 C7 Cell Structure & Function Nucleus – (plural, nuclei) large membrane-enclosed structure containing DNA. The DNA appears granular most of the time and is called chromatin. When the cell is dividing the chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. 2 C7 Cell Structure & Function Nuclear envelope – double membrane with pores surrounding nucleus. Nucleolus – dense region of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. Organelles – membrane bound structure in eukaryotes that carries out some function for the cell, ex. nucleus, mitochondria Cytoplasm – gel-like substance outside the nucleus. Ribosomes – small particles of RNA and protein where proteins are made in the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – site where lipids and proteins are assembled. These materials are exported from the cell or become part of cell membrane. Rough ER – has ribosomes and makes proteins. Smooth ER – has no ribosomes and makes lipids or detoxifies. 3 C7 Cell Structure & Function Golgi apparatus – modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage in the cell or secretion from the cell. 4 C7 Cell Structure & Function Lysosomes – enzyme filled organelles that digest food for the cell and get rid of old organelles. Vacuoles – store materials like water or nutrients. Mitochondria – help convert food energy into cellular energy. Chloroplasts – in plants and some Protists, capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy (photosynthesis). 5 C7 Cell Structure & Function Cytoskeleton – network of protein filaments that maintain the cell’s shape and aid in movement. Centrioles – help organize cell division, (not found in plants). Cilia – short projections made from the microtubules that function in movement. Flagella – long projections from the microtubules that aid in movement. 6 C7 Cell Structure & Function Cell wall – provides support & protection in bacteria, plants, fungi, and some Protists. Made of cellulose in plants. NOT in animal cells. Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) – regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support. Found in ALL cells. Made of phospholipids. Unicellular organisms – when one cell is the organism, ex. Bacteria and many Protists. 7 C7 Cell Structure & Function Multicellular organisms have many cells that are specialized. Cell differentiation or cell specialization - when cells develop in alternative ways to perform different tasks, “Go Go Stem Cells” ex. Red blood cells are specialized to transport oxygen. Pancreatic cells produce certain proteins. Guard cells in plants open and close the stomata.(link to stem cell animation) Cell –collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier; basic unit of life. Tissues – group of similar cells that perform a particular function. Organ – many groups of tissues work together to function as an organ. Organ system – a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function, like digestion. Diffusion through cell membranes: Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. (Requires NO energy). 8 C7 Cell Structure & Function Concentration – mass/volume. Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Isotonic – concentrations are the same on both sides of the membrane. Hypertonic – more concentrated. Hypotonic – less concentrated. 9 C7 Cell Structure & Function Facilitated diffusion – diffusion through protein channels without using energy. Active Transport – movement of particles that takes energy. 10 C7 Cell Structure & Function Passive Transport – movement of particles without using energy. Endocytosis – taking material into a cell by engulfment, (takes energy). Phagocytosis – taking in food or solid particles. Exocytosis – releasing material from a cell, (takes energy). 11