* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Notes
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
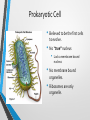
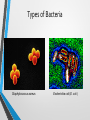
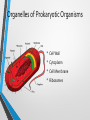
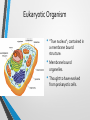
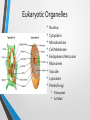
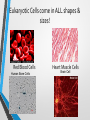
Comparing Prokaryotic Cells with Eukaryotic Cells • Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. • "Karyose" comes from a Greek word which means "kernel," as in a kernel of grain. In biology, we use this word root to refer to the nucleus of a cell. • "Pro" means "before," and "eu" means "true," or "good." So "Prokaryotic" means "before a nucleus," and "eukaryotic" means "possessing a true nucleus." Prokaryotic Cell • Believed to be the first cells to evolve. • No “true” nucleus • Lack a membrane bound nucleus • No membrane bound organelles. • Ribosomes are only organelle. Prokaryotic Organisms • • • • • Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms The largest group of organisms, mostly due to the vast assortment of bacteria which comprise the bulk of the prokaryote classification. Kingdom Monera has been SPLITArchaebacteria, Eubacteria Archaebacteria-hot springs, deep ocean vents • Halobacterium, Thermophiles Eubacteria- everywhere • Examples: Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli (E. coli), Streptococcus Types of Bacteria Coccus Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus Escherichia coli (E. coli ) Organelles of Prokaryotic Organisms • Cell Wall • Cytoplasm • Cell Membrane • Ribosomes Eukaryotic Organism • “True nucleus”; contained in a membrane bound structure. • Membrane bound organelles. • Thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic Cell • • • • • Eukaryotes are generally more advanced than prokaryotes. ALL multicellular organisms contain eukaryotic cells Kingdoms:Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia Protista-UNICELLULAR • Examples: Paramecium, Euglena, Amoeba (Yeast-Fungi) Fungi, Plantae, AnimaliaMULTICELLULAR • Examples: Mushroom, Moss, Salmon Eukaryotic Organelles • • • • • • • • • Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Cell Membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Vacuole Lysosome Plants/Fungi • • Chloroplast Cell Wall Eukaryotic Cells come in ALL shapes & sizes! Red Blood Cells Human Bone Cells Heart Muscle Cells Brain Cell