* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download O - morescience
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
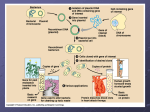
Protein Transformation Lab Intro UCSD: BioBridge Program E. coli By Lynn More - Olympian High School along with UCSD What is Transformation? Bacterial chromosome Uptake of foreign DNA, often a circular plasmid Plasmid Bacterial chromosome Plasmid Bacteria now express cloned fluorescent protein (transcription of gene and translation of mRNA to protein at ribosomes). Allow bacteria to grow for 1-3 days on plate with ampicillin. What is protein transformation? Introducing DNA that expresses preferred gene(s) into a host. Why do protein transformation 1. Inhibit or silence the expression of a gene i.e. - allows you to determine its function or importance 2. Carry out certain functions i.e. - make insulin, clot blood, resist pests, resist antibiotics, eat oil 3. Used as markers to track the location and function of the gene i.e. - fluorescent proteins Aequorea victoria and Discovery of GFP1960’s OSAMU SHIMOMURA Co-winner of Nobel Prize There are three amino acids which are critical for GFP’s green fluorescent color. Only a 1 amino acid difference changes green to blue, and blue to cyan. Fluorescent Proteins-Applications •Transgenic Mice Neuron Transgenic Zebra Fish Roger Tsien and Rainbow Proteins 17 Mut mgrape 1 6 Mut DsRed.T 1 33 Mut Dimer 2 6 Mut 3 Mut mHoneydew mCherry mRFP1 4 Mut 8 Mut 3 Mut 7 Mut mStrawberry mBanana mOrange mTangerine Cellular organelles “marked” with FPs Human cell stained with two different fluorescent proteins to visulalize cytoskeletal components. Transfected with GFP-tubulin / mCherry actin (Ben Giepmans) C Elegans transfected with GFP tubulin construct (Susan Kline) The rainbow of mFruit Fluorescent Proteins http://www.dnai.org/a/index.html Central Dogma DNA---> mRNA---> Protein---> Trait Materials 4 microcentrifuge tubes 2 Empty (clear/colorless) CaCl2 on ice (blue) either PM1 or PM2 on ice. (clear/colorless) 4 disposable transfer pipette 1 Inoculating loops 3 Q-Tips LB plates (2 LB/Amp - red line, 1 LB no Amp) Lab station waste containers - one with 10% bleach, other empty Equipment: 42˚C for 45 seconds Vortex Hot water bath Incubator 37˚C / 98.6˚F Human body temperature Label your equipment LB/AMP + P5 Table ? A+ LB/AMP - P5 LB/No AMP - P5 Table ? A- Table ? What is a plasmid? • • PM means Plasmid Mix What: A small circular piece of DNA naturally occurring in bacteria PM1 Green Blue Grape Why: Can be altered in lab to express protein of interest. PM2 Cherry Tangerine Banana promoter GFP Origin Gene of Interest: AMPR - Ampicillin Resistance Gene Antibiotic Resistance AmpR Stop Gene of Interest: Fluorescent Protein Escherichia coli • What? • AKA (also known as) E. coli • Prokaryote • Single-celled organism • No nucleus • No membrane –bound organelles • Why? • Small, so only need… • Food (LB Agar) • Little space • Warm temps (37˚C) • Little humidity • • • Reproduces fast • Binary fission • x 106 Can uptake foreign DNA Clones itself & its contents Why calcium chloride? • Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) Transformation solution • CaCl2 is necessary because: • The positive charge of Ca++ ions neutralizes DNA’s slightly negative charge • increases the diffusion of its foreign genetic information through the cell wall and cell membrane into the bacteria. Ca++ Ca++ O O P O O CH2 Base O Sugar O Ca++ O P O Base O CH2 O Sugar OH Pipette Techniques 1.0 mL • Squeeze the bulb with two fingers - firmly - hold • Insert into the fluid • Gently release SOME pressure on the bulb! Until the liquid gets to the 0.1 m mark 0.5 mL • Maintain the pressure If you release all pressure the 0.25 mL fluid will be sucked up into the bulb rather than to the measurement line. 0.1 mL • Move the pipette to the microcentrifuge tube • Squeeze the fluid from the pipette into the tube. • Repeat, measuring to 0.25 mL • Add the liquid to the microcentrifuge tube • Repeat measuring 0.5 mL, then • Add the liquid to the microcentrifuge tube • Move 1.0 mL into the pipette then to the microcentrifuge tube • Cap, Mix with rocking & vortex, empty and returnL The what’s and why’s of Heat Shock • Incubate on ice (10 minutes) slows fluid cell membrane (constricts pore size) • Heat-shock (42˚C for 45 seconds) increases permeability of membranes (dilates/opens pores, allowing the plasmid to get inside the bacteria) • Incubate on ice (2 minutes) slows fluid cell membrane (reduces permeability again, “locking” the plasmid inside the bacteria) Plate Streaking Techniques Purpose is to spread out the bacteria so it has access to more food and space Plasmid = a vector that carries genetically engineered DNA segment into a host cell. Recombinant DNA Insert the DNA (plasmid) Using a Heat Shock Method Bacteria cell Bacterial chromosome Bacteria plated on LB agar + antibiotic cloning X 106 Collect culture Only bacteria containing Recombinant DNA grow DNA Purification Why Ampicillin? • Ampicillin inhibits cell growth. Only cells that can inactivate the ampicillin around them will grow. • Ampicillin resistance fluorescent protein gene is tied to (expressed with) the • Ampicillin is a selection mechanism that only allows transformed bacteria to grow on the plate Satellite Colonies Regular bacteria wh Are eating the food t has been treated wit the enzyme - and no Not poisonous to the Genetically Modified E. Coli Bacteria Region around Modified Bacteria where enzyme has Broken down the antibiotic Agar What’s happening in the petri dish? Represents _________________________________________ LB Agar - a nutrient substrate to encourage growth Represent ___________________________________________ Ampicillin - an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth Represent ______________ Bacteria growth Bacteria killed by ampicillin ______________________ Represent _________________________________ Genetically transformed bacteria that are: 1. Resistant (or shielded) from the effects of ampicillin 2. Marked with a Fluorescent Protein Ampicillin acts as a __________________ selection mechanism that only allows ___________ transformed bacteria to _____ grow on the plate Transformation Prep.ppt Make two Plasmids Glue/Tape Glue/Tape Pick a Fluorescent Protein gene to insert Restriction Enzyme mCherry mTangerine mBanana GFP BFP Green Fluorescent Protein Blue Fluorescent Protein mGrape mPlum Use DNA Ligase (tape or glue) to bond the gene of interest Restriction Enzyme Restriction Enzyme Add an antibiotic resistance gene to both plasmids you make. Restriction Enzyme AmpR gene TetraR gene KanR gene PenR Ampicillin Tetracycline resistance Kanamycin resistance Penicillin resistance resistance gene Time to make the second Plasmid Model Restriction Enzyme Use DNA Ligase (tape or glue) to bond the gene of interest Restriction Enzyme Tuck Under & Glue/Tape Pick a gene of interest to add to the second plasmid you make Insulin gene Save a diabetic Factor VIII gene Save a hemophiliac Pest Resistance Oil Spill gene gene Save a plant Save an environmen t Congratulations scientists you have just made recombinant DNA: genetically engineered DNA with genes that can save lives! Tuck Under & Glue/Tape Make a Plasmid Activity #? 1. Cut the DNA with a _______________ (Scissors) 2. My gene of interest was (FP - ________ & __________) 3. My goal is to (FP) - track ____________; save ________ 4. The petri dish would have: ___________ antibiotic; ___________ antibiotic so…I need to make the transformed bacteria resistant to that antibiotic (_____); (_____) 5. What I have made are 2 small circular pieces of DNA with two genes of interest each & they called plasmids. Bioluminescence vs. Fluorescence Bioluminescence Fluorescence http://fireflyforest.net/firefly/2006/11/13/fluorescent-scorpion-in-uv-light/ Natural Light Scorpion- Natural Light Scorpion- UV Light In the Dark Bioluminescent organism produces its own light. A fluorescent organism absorbs light at one wavelength (UV) and a reemits the light at a visible wavelength= color The plasmids we have… The plasmid serves as a carrier or transporter of a genetically engineered DNA segment into a host cell. Area of Interest - Fluorescent Protein Gene for antibiotic resistance Restriction Enzyme Restriction Enzyme Cuts the DNA Foreign DNA Sticky ends help attach to the plasmid DNA Ligase Recombinant DNA EcoRI (pronounced "eco R one") is a commonly used restriction enzyme isolated from certain strains of E. coli used to cut DNA at specific locations.