* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transformation Chapter 13-3
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
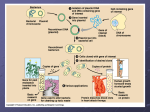
Cell Transformation Chapter 13-3 I. Bacterial Transformation – using a bacteria cell to produce proteins from other organisms (ex. Insulin for diabetics) A. Bacterial DNA forms a round loop called a Plasmid B. Genetic Marker- can be a gene for antibiotic resistance that is spliced onto the gene that researchers want expressed. 1. Use a restriction enzyme to cut plasmid and use same enzyme to cut out segment of DNA 2. This creates ends with nucleotides that match “sticky ends” 3. Allows bacteria with the gene to be separated from bacteria that don’t 4. After bacteria cells reproduce the protein, the protein can be removed and purified for use II. Plant Transformation- A gene can be inserted into a plant cell using a modified DNA (bacterial) plasmid and an inactive tumor producing gene. III. Animal Transformation- Using similar techniques, genes can be inserted into animal cells.