* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Selective Breeding
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
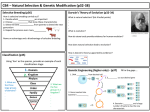
Mind Stretcher- 3/1/16 1.A change in the DNA sequence that can be harmful, helpful or make no difference A.Ribosome B.Messenger RNA C.Mutation D.Transfer RNA Selective Breeding S7L3. Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. c. Recognize that selective breeding can produce plants or animals with desired traits • ”Know” Selective Breeding… –choosing two organisms of the same species to mate with the hope of getting the best qualities of each parent to show up in the offspring. –Also called “Artificial Selection” Selective Breeding: Details • Selective breeding is used mostly for dogs, cats, other pets, cattle, and crops. Selective Breeding Example A “Robust” means STRONG & HEALTHY! Tough wild boars mated with friendly meaty pigs give you robust & meaty pigs for your farm. Tough Boar + Meaty Pig = Superpig (strong, tough, meaty pig) Selective Breeding Example B Brahman cattle: Good resistance to heat, but poor beef. English shorthorn cattle: Good beef but poor heat resistance. Santa Gertrudis cattle (cross of 2 breeds) RESULT = good beef and resistant to heat! hot weather cow + beefy cow = (beefy/hot weather cow) Selective Breeding: Example C Ancient corn from Peru (~4000 yrs old) Choosing only the best corn plants to use for future seeds = better crops over time. Selective Breeding Example D X = little red + big green = BIG RED TOMATO Remember: • Selective breeding crosses (mates) organisms with desirable traits to produce offspring that have the traits from both parents! Advantages of Selective Breeding • Might get improved organisms • Don’t need any special tools or lab • Can be performed easily by farmers & breeders Disadvantages of Selective Breeding • Undesirable traits from both parents may appear in the offspring • Disease can accumulate in the population – deaf dalmatians, boxers with heart disease, labs with hip problems, etc. • Genetic disorders become more prominent due to Inbreeding (breeding of closely related family members to increase a particular trait) Selectively Breeding Cows • You may one breed each cow only one time • You must say which trait you are hoping to pass on for each cow. EX: I chose Alma for her resistance to weather and I chose the bull, Brutus, for his strong muscles. Ticket out the Door • On your device, login to https://b.socrative.com • Type in Room # 53388 #1- Name • #2- What you learned (1-2 sentences) #3- True or False? Selective breeding changes the DNA of an organism (the offspring) over generations. **Take turns with the 9 ipads or desktop computer if your device doesn’t load Socrative. Selective Breeding- PowToons presentation https://youtu.be/CDnsj25h0Ek REVIEW • Genetic Engineering – Keep this side blank…we will complete it soon! • Selective Breeding – Process has been around for thousands of years – Combines the best traits of two organisms – Results in organisms that have the desirable traits of their parents Genetic Engineering Everything you need to know! S7L3. Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. c. Recognize that selective breeding can produce plants or animals with desired traits • Know –GE involves identifying certain genes and moving them from one organism to another – even to a different species or removing the gene entirely! Did You Know? Scientists used a bioluminescent gene from a jellyfish to create “glowing” green mice! Genetic Engineering: Details • It produces an organism that has a new trait it would most likely not have developed on its own • Genetic engineering is controversial. Genetic Engineering Example A: Give the insulin gene to diabetics. • Diabetic = a person whose pancreas cannot create the important hormone insulin. 1. Take the gene for making insulin from a healthy donor’s DNA 2. Add that gene to the DNA of pancreas cells from a diabetic 3. Let mitosis happen for a while (in a “test tube”) so you get LOTS of pancreas cells with the good gene. 4. Surgically implant the good cells back into the diabetic Genetic Engineering Example B: Give tomatoes the ability to make anti-freeze. • Placing the “anti-freeze gene” from a fish in tomatoes so the tomatoes can still grow in cold weather. Genetic Engineering Example C: Make chickens with • Scientists engineered chickens to be featherless by REMOVING the no feathers. gene in chicken DNA that causes them to grow feathers Genetic Engineering Example D: Cabbage plant + scorpion venom = bug-proof veggies Scientists added a gene for producing scorpion venom to cabbage plants to kill pesky caterpillars that eat crops! Remember! Gene: a segment of DNA Genetic engineering involves the manipulation of genes! What is a Genetically Modified Food? https://youtu.be/JMPE5wlB3Zk Using the DNA Sequence • Knowing the sequence of an organisms DNA (Genome) allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. Genetic Engineering of insectresistant corn #2 Use enzymes to cut desired gene loose #1 Identify desired gene #3 Remove undesired gene #4 Insert desired gene into corn Different techniques are used to… • Extract DNA from cells • Cut DNA into smaller pieces • Identify the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule • Make unlimited copies of DNA DNA Extraction • DNA can be extracted from most cells by a simple chemical procedure • The cells are opened and the DNA is separated from other parts of the cell Fun With Glow Genes • There is an enzyme that makes jellyfish and fireflies glow • Luciferase • Could we take a gene out of an animal and put it in something else? • Could we get things that don’t glow, to glow Glow - Fish Glow - Mice Advantages of Genetic Engineering • Will get improved organisms • Can create organisms with traits not previously thought possible • Can remove “bad” genes • Reduces the chance of getting “undesirable” organisms Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering • • • • • Co$tly Must be performed in a lab with special equipment Ethical issues Long term negative affects Negative environmental impacts Genetic engineering has few limits - except our imagination, and our moral or ethical code. Be Creative! • Think of an organism in which you’d like to enhance or modify. • Now select a specific “gene” or trait from another organism that you could insert into your first organism’s DNA. • Draw a picture and describe your genetically modified organism on your organizer. REVIEW • Genetic Engineering – Relatively new process performed within labs – Manipulates or alters the genetic makeup of organisms – Results in organisms with new traits • Selective Breeding – Process has been around for thousands of years – Combines the best traits of two organisms – Results in organisms that have the desirable traits of their parents Ticket out the Door • On your device, login to https://b.socrative.com • Type in Room # 53388 #1- Name • #2- What you learned (1-2 sentences) #3- True or False? Genetic engineering changes the DNA of an organism. Formative Assessment • Please write SB for selective breeding or GE for genetic engineering. • **Two answers will actually be both SB/GE…can you determine which two? Scientific Example or Fact Farmers removed the gene in chicken DNA to make them grow featherless. This process attempts to combines the best traits of 2 parents. Dog breeders wanted to breed a dog that would run fast but also be born with long, shiny fur, looking for the best characteristics from the parents. Scientists take out a gene for bioluminescence from a jellyfish and put that gene into a mouse’s DNA to see if it will have a glowing effect. This process is relatively new and done in science labs. This process manipulates or alters the genes/DNA of organisms. This results in organisms with new traits. English Shorthorn cattle, which produced good beef were bred with Brahman cattle from India to make the offspring both tasty and resistant to heat and humidity. This process has been around for thousands of years. Scientists removed a gene for fat in bison to make them leaner. This results in organisms with desirable traits from both parents GE or SB? Scientific Example or Fact GE or SB? 1. Farmers removed the gene in chicken DNA to make them grow featherless. GE 2. This process attempts to combines the best traits of 2 parents. SB 3. Dog breeders wanted to breed a dog that would run fast but also be born with long, shiny fur, looking for the best characteristics from the parents. SB 4. Scientists take out a gene for bioluminescence from a jellyfish and put that gene into a mouse’s DNA to see if it will have a glowing effect. GE 5. This process is relatively new and done in science labs. GE 6. This process manipulates or alters the genes/DNA of organisms. BOTH 7. This results in organisms with new traits. BOTH 8. English Shorthorn cattle, which produced good beef were bred with Brahman cattle from India to make the offspring both tasty and resistant to heat and humidity. SB 9. This process has been around for thousands of years. SB 10. Scientists removed a gene for fat in bison to make them leaner. GE 11. This results in organisms with desirable traits from both parents SB