* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recombinant DNA and Cloning The Impact of Biotechnology
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
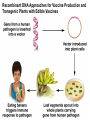
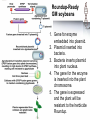
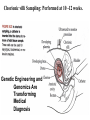
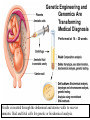
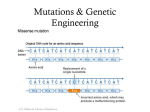
Recombinant DNA and Cloning The Impact of Biotechnology Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Terms to Know • Restriction enzymes: allow the DNA to be cut and spliced at VERY specific locations. • Vectors: carriers of DNA molecules; usually bacteria. • Plasmid: circular DNA found in bacteria. • Recombinant DNA: original carrier DNA + introduced sections of DNA. • Clones: when the bacteria divide, millions of copies of the original recombinant DNA are made. Impact of Biotechnology • Biotechnology: use of modified organisms or their products to enhance our lives. • Ethical Dilemmas: – Patenting genes for ownership. • Patents offer scientists a chance to fund further research. – Limited availability of seeds to farmers. • Concentrates crop ownership to biotech companies, out of farmer’s hands. – Impact of GM foods in our own bodies. • Enough testing to identify risks/benefits? • Biotech and Medicine: – Too much information too early? – Inability to get medical insurance. Genetically Engineered Organisms Synthesize a Wide Range of Biological and Pharmaceutical Products Figure 24.1 Genetically Modified Plants • Resistance to insects, weeds, and viruses. • Enhanced oil content. • Delayed ripening. • Over a dozen genetically modified crops approved to grow in the US. – 45% of US corn crop. – 85% of soybean crop. • 60% of processed food contains GM foods. • GM foods can also be modified to increase the nutritional content of foods. – GM rice (golden rice) has been modified to contain more of the building blocks needed to produce Vitamin A. – Reduced blindness in poorer nations. GM Animals • Embryo splitting has created commercially cloned GM organisms for 25 years. • Don’t have to wait until adulthood to see if desired traits were inherited. • Cloned for desirable traits such as: – High milk production. – Speed in race horses. – Transgenic animals. • Transgenic animals are produced when one animal’s desired traits are recombined into another animal. – Human genes transferred into sheep for production of human proteins. Table 24.1 Recombinant DNA Approaches for Vaccine Production and Transgenic Plants with Edible Vaccines Figure 24.2 During the past 10 year s, transgenic crops have been rapidly adopted in both industrialized and developing countries. Roundup-Ready GM soybeans 1. Gene for enzyme embedded into plasmid. 2. Plasmid inserted into bacteria. 3. Bacteria inserts plasmid into plant nucleus. 4. The gene for the enzyme is inserted into the plant chromosome. 5. The gene is expressed and the plant will be resistant to the herbicide Roundup. GM Roundup resistant soybean plants. Allows Roundup to be applied to the crop to kill weeds but not harm the soybean. Golden Rice • genetically modified to produce -carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. • Many children in countries where rice is a dietary staple lose their eyesight because of diets deficient in vitamin A. Transgenic Atlantic salmon (bottom) overexpressing a growth hormone (GH) gene . GloFish, marketed as the world’s first GM-pet Chorionic villi Sampling: Performed at 10 -12 weeks. Genetic Engineering and Genomics Are Transforming Medical Diagnosis Genetic Engineering and Genomics Are Transforming Medical Diagnosis Performed at 14 – 20 weeks Needle is inserted through the abdominal and uterine walls to recover amniotic fluid and fetal cells for genetic or biochemical analysis. A single cell from an earlystage human embryo created by in vitro fertilization can be removed and subjected to preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). Text Reading • On own, read Model Organisms to understand how genetics can be studied through the use of model organisms. • What are examples of Model Organisms? • What makes a good Model Organism? Chapter 1 Essential Points • • • • Page 4: #1: Mendel’s Work. Page 5: #2: Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Page 8: #3: Central Dogma of Biology Page 12: #4: Biotech has revolutionized agriculture and pharmaceutical industries. Genetic testing and gene therapy has impacted how we treat and diagnose genetic diseases. #5: Recombinant DNA technology has given rise to several new fields in science. • Page 14: #6: Using model organisms allows us to use genetics and biotech to understand human health. #7: Policies and regulations that pertain to genetic technology is lagging behind the technologies that are being introduced.