* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis - Simon Technology
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
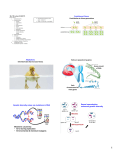
Protein Synthesis Mutations and Genetic Disorders Standards: BI4. c. Students know how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the gene or the sequence of amino acids in an encoded protein. BI5. c. Students know how genetic engineering (biotechnology) is used to produce novel biomedical and agricultural products. BI5. a. Students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. Objectives: explain the genetic factors that influence the way we look. recognize that DNA contains the genetic information that determines the way we look. explain the structure and function of DNA, RNA, and proteins. predict the physical characteristics of an organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. explain the causes of gene and chromosomal mutations in multicellular organisms. understand how changes in DNA sequences can cause changes in the proteins that are produced. Review-What is the central dogma? The central dogma describes the flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins. Review-How does your DNA determine what you look like at the molecular level? Your traits are determined by your DNA because your DNA has codes/instructions for your traits called genes. Genes contain the codes for proteins, which make-up many structures such as your fingernails, hemoglobin, muscles, and the color of your eyes. The process of converting the instructions of your traits from your genes into protein molecules is called protein synthesis. Mutations!!!!!!!! What happens when protein synthesis doesn’t work properly? When there is a change in an organism’s DNA this can change the organism’s phenotype. By changing the DNA sequence we are changing the “instructions” for proteins and this can change an organism at the molecular level. This is similar to what happens when you change a step in a recipe or shift the reading frame in a sentence. These changes alter the product. Gene Mutations Changes in a single gene Point mutations=occur at a single point in the nucleotide, change one amino acid in a protein, substitution Frameshift= insertion or deletion of a nucleotide, shift reading frame of amino acids, alters function of proteins Point and Frameshift Mutations Point= Biology is so much fun. Biology is so much dog. Frameshift= The cat ate the rat. Thc ata tet her at. Chromosomal Mutations Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes Can change the location or number of copies of some genes Deletion, Duplication, Inversion, Translocation What are genetic disorders? A genetic disorder, or genetic disease is a disease caused by abnormal expression of one or more genes in a person causing a phenotype. Genetic Disorders PKU- metabolic disease, affects the way body processes one of the building blocks of protein Osteogenesis Imperfecta- bone structure is not produced properly Achondroplasia- dwarfism Trisomy 21-three chromosome 21’s, Down Syndrome Achondroplasia Osteogenesis Imperfecta Individuals with DS Hemophilia Sickle Cell Anemia Albinism Summary Questions: What happens when protein synthesis doesn’t work properly? How do gene mutations cause changes in the proteins that are produced? What are chromosomal mutations? How do genetic changes (DNA sequences, chromosome #) cause changes in the proteins that are produced?