* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to DNA - University of Dayton
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
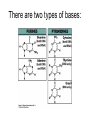
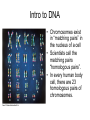
Introduction to DNA Question: • From your on-line computer activity, what do you know about the structure of DNA? Structure of DNA • DNA is a polymer of what???? Nuclotides! There are two types of bases: Adenine & Guanine (A&G)= Thymine & Cytosine ( T & C) = There are two types of bases: Intro to DNA • Chromosomes exist in “matching pairs” in the nucleus of a cell • Scientists call the matching pairs “homologous pairs”. • In every human body cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. Example of a human Karyotype IN HUMANS Pair # 1- 22 = “autosomes” Pair #23 = “Sex chromosomes” * XX = * XY = Karyotype • What does the prefix “homo” mean? • How are homologs similar? #1 #2 #3 #4 Karyotype Q: How are homologs different???? • GENE – A: IMPORTANT !! • All 46 chromosomes are present in every human body cell!!! Therefore • All 30,000 genes pairs which make up a human are in every human body cell! IMPORTANT !! • Genome – • *** Every body cell of an organism contains its entire genome !!!! *****