* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab Exercise #17
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
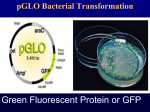
Bio 112 Genetics Lab Exercise 17 Dihybrid Cross in Corn There are four grain phenotypes in the above ear of corn: Purple & Starchy(A), Purple & Sweet(B), Yellow & Starchy(C) and Yellow & Sweet(D). These four grain phenotypes are produced by the following two pairs of heterozygous genes (R & r and SU & su) located on two pairs of homologous chromosomes (each gene on a separate chromosome): Dominant alleles Recessive alleles R = Purple r = Yellow SU = Starchy su = Shrunken The cross which produced the corn ear above was: Rr SUsu X Rr SUsu DNA Extraction from Bacteria Transformation of Bacteria (pGLO) We will introduce a gene into E. coli that will produce a protein (green fluorescent protein-GFP) that will cause the colonies to glow green when exposed to ultraviolet light What is Transformation? Uptake of DNA (in this case a plasmid pGLO) from the surrounding environment of the cell. What is Green Fluorescent ProteinGFP)? GFP was discovered in the bioluminescent jelly Aequorea victoria. The gene that makes this protein is used extensively in research…and also for fun? Transformation Procedure … in a nutshell. • Suspend bacterial colonies in Transformation Solution, CaCl2 • Add pGLO plasmid DNA to +DNA tube • Place tubes on ice • Heat shock at 42oC and place on ice • Incubate with LB broth • Streak plates Expected Results Our genes of interest: amp…araC…GFP araC ori pGLO bla GFP amp – this gene will give our transgenic bacteria resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin araC – this gene will produce a protein which in the presence of the sugar arabinose will allow the bacteria to turn on the GFP gene GFP – in the presence of arabinose, this gene will “turn on” and cause the transformed (transgenic) bacteria to glow green The Role of Arabinose • The bacterial genes that make the digestive enzymes needed to break down arabinose for food are not expressed (made) when arabinose is absent. • When arabinose is present the genes are turned “on”. When it is absent the genes remain “off”. • Arabinose initiates transcription of the genes by promoting the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. araC ori pGLO bla GFP Expected Results