* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia tolerance in
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
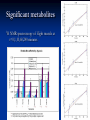
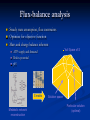
Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia tolerance in Drosophila flight muscle: metabolomic and computational systems analysis Jacob Feala1,2 Laurence Coquin, PhD2 Andrew McCulloch, PhD1 Giovanni Paternostro, PhD1,2 1) UCSD Bioengineering 2) Burnham Institute for Medical Research Cellular hypoxia response Hypoxia is the cause of cell death in many pathologies, mechanism not known All cells have intrinsic defenses Hypoxia tolerant organisms have highly orchestrated metabolic regulation Drosophila as a model for hypoxia research Flies are hypoxia tolerant Simple system, genetic tools and libraries Genetic screen found gene required for tolerance 1 Hypoxia tolerance gene was successfully transferred to mammalian cells 2 human fly 1Haddad GG et. al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 30;94(20):10809-12. 2Chen Q et. al., J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49113-8. Epub 2003 Sep 16. Phylogenetic tree Systems analysis of hypoxia response Complex balances must be maintained to tolerate hypoxia ATP supply and demand Redox potential Metabolic intermediates pH Systems biology to understand and model the complex control systems Hochachka, P. W. J Exp Biol 2003; 206:2001-2009 General hypothesis for hypoxia tolerance Flexible metabolic regulation is the major source of hypoxia tolerance Immediate (minutes) Global (ATP production, biosynthesis, protein translation) Our systems approach to modeling ATPgenerating metabolism: Metabolomics to find all anaerobic pathways Flux-balance analysis to simulate pathways under varying oxygen Generate novel, specific, testable hypotheses for hypoxia tolerance 1H NMR spectroscopy of hypoxic fly muscle • 0.5% O2 • 240 minutes • supervised by Laurence Coquin MAMMALIAN TISSUE: Troy H et. al. Metabolomics 2005; 1: 293-303 Global metabolic profile • Concentrations measured by targeted profiling (Chenomx): peak identification, alignment, subtraction • Lower confidence group due to spectra overlap Significant metabolites 1H NMR spectroscopy of flight muscle at t=0,1,10,60,240 minutes Reconstructing the Drosophila metabolic network Database integration KEGG: metabolic genes, enzymes, reactions, EC numbers, pathways Flybase: complete genome, proteins, function, compartment, mutant stocks, references Filtered gene index Pathways 109 EC numbers 437 Genes 1322 Genes (mitochondrial) 125 Genes (stocks available) 507 Reconstructing the network Network model of central metabolism 162 genes, 143 proteins and 158 reactions Includes glycolysis, TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, β-oxidation, amino acids Elementally- and chargeStoichiometric balanced matrix Metabolic network reconstruction Literature and Databases Gene-protein-reaction associations Annotated Genome Reed JL et. al., Nat Rev Genet. 2006 Feb;7(2):130-41. Drosophila central metabolism Main energetic pathways in model Glucose NADH Acetate NH4 NADH α-Oxoglutarate Glycolysis ATP Glutamate ATP NADH Pyruvate Alanine Lactate Acetyl-CoA α-GPDH shuttle NADH Cytosol Mitochondria Pyruvate Acyl-carnitine shuttle FADH NADH CO2 Acetyl-CoA Oxaloacetate Known Drosophila pathways ATP Citrate TCA cycle NADH/FADH2 CO2 ATP O2 H2O Oxidative phosphorylation Hypothesized pathways Products seen in NMR NADH/FADH2 Flux-balance analysis Steady state assumption, flux constraints Optimize for objective function Mass and charge balance inherent Null Space of S ATP supply and demand Redox potential pH S matrix Metabolic network reconstruction Solution space Particular solution (optimal) glc Flux-balance analysis of hypoxia Simulation conditions ac lac ala - Glucose (and equivalents) only carbon substrate - Lactate, alanine, acetate constrained to NMR fluxes - Varied O2 uptake constraint - Objective: maximize ATP production Hypoxia simulation: key fluxes (Pseudo-) Mammalian Drosophila Stable pH Reduced glucose uptake Equivalent ATP Abbreviations: • atp: ATP production • co2: CO2 production • glc: glucose uptake • h: proton production • ac: acetate accumulation • lac: lactate accumulation • ala: alanine accumulation Conclusions ‘Exotic’ anaerobic pyruvate pathways in fly may contribute to hypoxia tolerance New hypotheses to test: alanine and acetate production essential under hypoxia Systems modeling revealed emergent behavior Perturbation Analysis of Energy Metabolism in Hypoxia Model Genetic perturbation Experiment Validate Refine NMR metabolomics Candidate genes Acknowledgements Polly Huang Palsson lab, UCSD Bioengineering Adam Feist Thuy Vo Khoi Pham Questions Flux variability