* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothermia wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Targeted temperature management wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
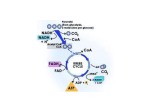
RAUSCH – Spring 2017 Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25 – Metabolism NOTE: We may not have time to cover all of these this term. Concentrate on questions involving what we actually covered in lecture. Some terms Know the definition and physiological/anatomical significance of the following: anabolic and catabolic reactions, anaerobic and aerobic metabolism, ATP synthetase, avenues of heat exchange (radiation, conduction, convection, evaporation), basal metabolic rate, beta-oxidation (of fatty acids), coenzyme A, direct and indirect calorimetry, electron transport chain, endergonic and exergonic reactions, FAD/FADH2, feedforward control, feeding and satiety centers, fever, glycolysis, heat gain and heat loss mechanisms, heat vs. temperature, hyperthermia, hypothalamic thermostat, hypothermia, Krebs’ cycle (TCA or citric acid cycle), lactic acid (lactate), metabolic rate, metabolic water, metabolism, minerals, mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane, NAD+/NADH + H+, nutrient, oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate-to-acetate step, reduction, substrate level phosphorylation, thermoneutral zone Study suggestions and potential essay questions What is meant by the term substrate level phosphorylation? What is meant by the term oxidative phosphorylation? Where in the cell does each of these processes occur? • electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) • glycolysis • Krebs’ cycle If glucose is the substrate, what goes in and what comes out of each stage of aerobic cellular respiration? (See Energy Statement handout for “stages.”) E.g., glucose, 2 ATP and 2 NAD+ enter glycolysis; 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH + H+, and 4 ATP are produced by glycolytic reactions. Why must you inhale oxygen to stay alive? I.e., what is oxygen’s role/function in aerobic cellular respiration? What is the function of NAD+ and FAD? Why is less ATP produced for each FADH2 than for each NADH in the mitochondrion? What is the significance of the H+ gradient that exists across the mitochondrial inner membrane? What is/are the source(s) of the CO2 that comes out of your mouth when you exhale? Write a balance chemical formula for the aerobic metabolism of glucose. Assume that 36 moles of ATP are produced for each mole of glucose. RAUSCH – Spring 2017 List five (5) factors that would increase metabolic rate. Define the following terms as they relate to heat gain or loss: radiation, convection, conduction, evaporation. How is an increased body temperature due to exercise fundamentally different than an increased body temperature resulting from a fever? Describe the information conveyed in the graph below. A. What is meant by the term “thermoneutral zone?” B. What factors contribute to the increases in oxygen consumption seen when environmental (ambient) temperature is raised or lowered from the thermoneutral zone? C. Why does metabolic rate decline at very high or very low environmental temperatures? D. Why does body temperature eventually rise or fall as ambient temperature changes? [NOTE: This is not as difficult as you might first think. You just need to show your common sense and your ability to read a graph.] RAUSCH – Spring 2017 Checkpoint questions Page 938: 1. Define metabolism. 2. Define catabolism. 3. Define anabolism. Page 947: 5. NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to the production of two ATP molecules in the mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to the production of three ATP molecules. Why? 6. How would a decrease in the level of cytoplasmic NAD+ affect ATP production in mitochondria? Page 968: 20. What effect does peripheral vasoconstriction on a hot day have on an individual’s body temperature? 21. Why do infants have greater problems with thermoregulation than adults do?