* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
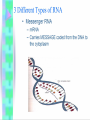
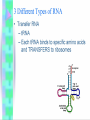
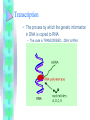
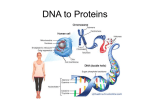
BIG PICTURE: MAKING PROTEINS • DNA RNA PROTEIN • Nucleus Cytoplasm Ribosomes WHY PROTEINS?? • Proteins are polymers = CHON – Proteins make up ENZYMES, muscles, hair, nails, and code for traits • Amino acids held together by peptide bonds – There are 20 amino acids in nature • Function of the protein depend on the twists and folds 8.4: Transfer of Genetic Information • DNA RNA • RNA: – – – – – Is Ribonucleic acid (isn’t missing the oxygen) Has RIBOSE as the sugar Can leave the nucleus to go to ribosomes Is single stranded No “T”s…has Uracil (U) bonding to A Transcription • The process by which the genetic information in DNA is copied to RNA – The code is TRANSCRIBED…DNA to RNA – In NUCLEUS f 8.5: Translation • The process of assembling proteins – RNA PROTEIN – Have to code for tRNA too which has an anticodon so the AA can be TRANSFERRED to ribosomes TOPIC: GENE EXPRESSION and GENETIC ENGINEERING • OBJECTIVE: LOOK AT BIOTECHNOLOGY (Ch 8.7-9.6) GENE EXPRESSION • Promoter – DNA segment that promotes transcription and recognizes mRNA (where transcription begins) • Structural Genes – Genes that code for particular proteins Controlling Gene Expression • Conserve resources • Only make proteins when needed*** Structure of Eukaryotic Gene • Promotor – Where transcription begins • Beyond the promotor – Introns • Sections of genes that do not code for amino acids; no proteins are made – Exons • Sections of genes that do code for amino acids, so proteins are made • Less than 10% of a human gene …… Mutations • Any mistake or change in the DNA sequence – Accuracy of DNA is important to ensure genetic continuity of new cells and offspring 3 types of mutations: • 1. Point mutations: change in ONE DNA base – This would change the meaning of the codon on the mRNA – Example: • THE DOG BIT THE CAT • THE DOG BIT THE CAR = mutation mutate d base 3 types of mutations: • 2. Frameshift mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA – This would cause every codon to be wrong from that point on in protein coding – Example: • THE CAT ATE THE FAT RAT • THE ATA TET HEF ATR ATT 3 types of mutations: • 3. Chromosomal mutations: – Affects the entire chromosome – If a chromosome is missing= monosomy • Monosomy on Sex Chromsomes = Turner Syndrome – 45 chromosomes in humans – May involve an extra chromosome = trisomy • Trisomy on Chromosome 21 is Down Syndrome – 47 chromosomes in humans CAUSES OF MUTATIONS • Mutations can be good, bad or nothing – They are usually random events but…. • Errors in DNA provide the variation that must be present for the evolution of species