* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operons - Haiku Learning
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
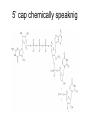
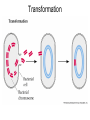
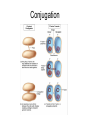
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes But first it’s QUIZ TIME!! Copier is down – deal with it 1. Write the correct mRNA transcript based on the gene sequence below: GTA GTA GGT 2. Use your codon chart to determine the sequence of amino acids dictated by the gene sequence above. mRNA AGA GGA AGC GCA CAG Amino Acid arginine glycine serine alanine glutamine 3. Which mRNA would code for both amino acid sequences shown, simply by a shift in the reading frame? …glutamine…glutamine…glutamine …serine… serine… serine A. AGUAGUAGUAGU C. GCUGCUGCUGCU B. AGCAGCAGCAGC D. GCAAGCGCAAGC Use the amino acid chart from question #3 …glycine…serine…glycine… 4. Which of the following DNA strands would code for the amino acid sequence shown above? A. ACTCCTTCT B. TCTCCGTCG C. CCGTCGACT D. CCTTCGCCT #5 and #6 5. An incoming tRNA would attach to which site on the ribosome? 6. If the tRNA anticodon is UUU, what amino acid will it bring to the growing peptide chain? #7 and #8 7. Spliceosomes cut out ______ and splice together ________ which get expressed. 8. Modifications to the ends of the mRNA transcript are required before leaving the nucleus. Which end (3’ or 5’) is modified with a Poly- A tail? II. RNA modification 5’ cap chemically speaknig The movie – yes there is a movie • http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/mr naprocessing/movie.htm Why Cap and Poly- A tail? • Protect the messenger! • exonucleases – protect but destroy • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/5'_cap III Bacteria genetics • Binary fission Prokaryotic variation in genetic make-up • Mutations • Genetic recombination – Transformation – Transduction – Conjugation Transformation Transduction Conjugation IV. Control of metabolic pathways A. Two ways 1. Vary the activity of the enzymes (inhibit them or promote their ability) – feedback inhibition pathways 2. Vary the # of enzymes present – regulate enzyme production at the gene expression level B. Gene regulation in bacteria • OPERONS! – Need to know that an operon is a section of DNA that contains genes for a protein – Need to know the parts and players Ex 1 – Lac Operon Ex 2 Tryptophan operon A closer look at the parts • A) promoter – site on DNA where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription • B) operator – the “on/off” switch, located between promoter and structural genes • C) structural genes – genes that code for a protein Important players • Repressor – a protein that when active will bind to the operator thus blocking transcription • Regulatory gene – the DNA sequence that codes for the repressor protein • Co-repressor – a molecule that attaches to an inactive repressor and makes it active • Inducer – a molecule that attaches to an active repressor and makes it inactive How they work together • Negative regulation • Positive regulation Negative regulation • Two examples – Lac operon – Tryptophan operon – best animation link ever