* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Method 1
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
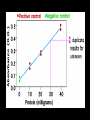
Quantitative of protein Huda Hania Methods of Quantitative of protein • Method 1: protein assay based on dye binding assay • Method 2: protein assay based on alkaline copper Method 1: protein assay based on dye binding assay • BRADFORD METHOD • Use of coomassie G-250 dye in a colorimetric reagent for the detection and quantitation of total protein . • In the acidic environment of the reagent, protein binds to the coomassie dye. • This results in a spectral shift from the reddish/brown form of the dye (absorbance maximum at 465nm) to the blue form of the dye (absorbance maximum at 610nm). • The difference between the two forms of the dye is greatest at 595nm, so that is the optimal wavelength to measure the blue color from the coomassie dye-protein complex • Development of color in coomassie dye-based (Bradford) protein assays has been associated with the presence of certain basic amino acids (primarily arginine, lysine and histidine) in the protein. • Free amino acids, peptides and low molecular weight proteins do not produce color with coomassie dye reagents. (unbound) forms are green or red. Samples treated with the Bradford assay. The brown sample (lower absorbance) contains no protein, while the blue sample (higher absorbance) contains protein. The amount of protein in the second sample can be determined by comparison to a standard curve • Advantages: This assay is quick, and the reagent is not affected by the presence of reducing agents, like DTT • Disadvantages: Basic conditions and detergents, such as SDS, can interfere with the dye’s ability to bind to the protein Biuret Test • Principle: • Under alkaline conditions substances containing two or more peptide bonds form a purple complex with copper salts in the reagent. • • Biuret Reagent contains: • Hydrated Copper sulphate – this provides the Cu (II) ions which form the chelate complex. Cu (II) ions give the reagent its characteristic blue color. • Potassium hydroxide does not participate in the reaction but provides the alkaline medium. • Potassium sodium tartrate (KNaC4H4O6·4H2O) stabilizes the chelate complex • The Biuret reaction can be used to measure the concentration of proteins because peptide bonds occur with the same frequency per amino acid in the peptide. • The intensity of the color, and hence the absorption at 540 nm, is directly proportional to the protein concentration, according to the Beer-Lambert law. tubes D.W Protein standard 1 0.5 0 0 2 0.4 0.1 0.4 3 0.3 0.2 0.8 4 0.2 0.3 1.2 5 0.1 0.4 1.6 6 0 0.5 2 Unknown 0 0 1. 2. 3. 4. Unknown 0.5 Add 1ml of biuret reagent to each tube and mix Incubation 30 min Read at 540 nm Draw the standard curve and measure the unknown Conc • A standard curve is a type of graph used as a quantitative research technique. Multiple samples with known properties are measured and graphed, which then allows the same properties to be determined for unknown samples by interpolation on the graph. The samples with known properties are the standards, and the graph is the standard curve. • For example, a standard curve for protein concentration is often created using known concentrations of bovine serum Reference range • Reference range for total proteins is 66.6 to 81.4 g/L