* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA damage/repair
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
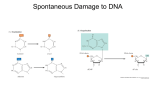
DNA Repair Lehninger, chapters 8 and 25 Blackburn & Gait, Ch. 6 and 8 Know main types of DNA damage Know repair mechanisms used for each type of damage Know the difference between transition and transversion Understand why defects in repair mechanisms could lead to cancers DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA damage from: 1. spontaneous loss of exocyclic amino group (deamination) C U occurs once every 107 C residues in a day (100x a day) A G (Hyp) occurs 100x slower 2. Hydrolysis of bond between sugar and base (apurinic residue) Occurs once every 105 purines in a day (10,000x a day) Slower for pyrimidines DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA damage from: 3. UV damage causes pyrimidine dimers DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA damage from: 4. Reactive chemicals Nitrous acid precursors Alkylating agents (nitrogen mustard, DMS, SAM) DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA damage from: 5. Oxidative Damage H2O2, •OH, •O2- DNA metabolism DNA Damage & Repair DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA metabolism DNA Repair In bacteria DNA metabolism DNA Repair DNA metabolism DNA Mismatch Repair Correction of mismatches increases fidelity by 100 to 1000-fold Repairs mismatches up to 1000 bp from hemimethylated GATC DNA Mismatch Repair DNA metabolism Binds all mismatches except C-C Binds to MutL-MutS and methylated GATC DNA metabolism DNA Mismatch Repair DNA metabolism DNA Base-excision Repair DNA glycosylases recognize deaminations and remove them leaving an apurinic/apyrimidinic site (AP site) DNA metabolism DNA Nucleotide-excision Repair Used to repair DNA lesions that cause large distortions in DNA helix (pyr dimers) DNA metabolism Photolyase DNA damage - mutation DNA damage - mutation DNA metabolism DNA SOS Repair Responds to extensive DNA damage, coordinated induction of a variety of genes DNA Repair DNA metabolism Defects in genes encoding proteins involved in mismatch repair, nucleotide-excision repair, and recombinational repair can cause cancer Nucleotide-excision repair sole repair pathway for pyrimidine dimers genetic defect causes XP, xeroderma pigmentosa, these individuals are extremely sensitive to sunlight and quickly develop sunlight-induced skin cancer Mismatch repair Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) linked to defects in these genes Defects in human MutL homolog, human MutS homolog Recombinational repair Recombination - linear sequence of DNA altered by cleavage and rejoining of chromosome (involves RecA protein) Repair of this type sometimes needed to reconstruct replication fork Human breast cancer genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) produce proteins that interact with the human homolog of RecA, therefore these are linked to recombination repair 10% of breast cancers have defects in BRCA1 or BRCA2 Women with defects in these genes have a >80% chance of developing breast cancer