* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download You Asked for it…..
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
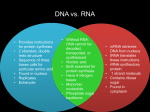
Biology REVIEW Building Block Uses Examples Test Carbohydrat Simple e sugars Ready source of energy Glucose Glycogen Cellulose Starch • Protein • • Transport Speed up reactions Immunity Cell communication Enzymes (-ase) Hemoglobin Antibodies Protein hormones (insulin) • Back up energy source In membrane Fats, oils • Leaves oily spot on brown paper bag Store and transmit genetic info DNA, RNA • DNA stains (methylene blue) Amino acids • • Lipid Fatty Acids • • Nucleic Acid Nucleotide • • STARCH turns black in iodine SUGARS react with Benedict’s Solution Reacts with Biuret Solution Turns purple PROKARYOTIC •Prokaryotic cells have DNA and ribosomes, but they have no internal membranes! (They don't have a nucleus) •They have ribosomes to make proteins •These are the simplest cells •Examples are bacteria, like those that cause strep throat. EUKARYOTIC • • • • • • Nucleus contains DNA Membrane bound organelles Ex/ Plant and animal These cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. Plant: Chloroplast and cell wall, box shape Animal: no cell wall, chloroplast, small vacuoles, has lysosomes • • • • • The plasma membrane surrounds EVERY cell. It is made of lipid and protein Phospholipid Bilayer It controls what goes in and out of a cell. Associated with HOMEOSTASIS Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Movement from high to low concentration Movement of water from high to low WATER concentration across a membrane Movement from LOW concentration to HIGH concentration No energy required No energy required USES ATP Converts energy in food (glucose) to ATP Cellular Respiration •Takes place in mitochondrion •Releases the energy stored in glucose •AKA aerobic respiration (NEEDS oxygen) Converts sunlight to chemical energy • • • • Requires oxygen Makes 32-36 ATP Produces carbon dioxide and water Happens in mitochondrion AEROBIC RESPIRATION •Does not use oxygen •Makes only 2 ATP • • Also called fermentation • • • Small amount of ATP YEASTS make ethyl alcohol BACTERIA and MUSCLE CELLS (w/o O2) make LACTIC ACID Happens in cytoplasm (cytosol) ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. • • • A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a sugar, a phosphate and one of four bases In DNA, the bases are A, T, C, and G DNA’s shape is a double helix • • • The two strands are held together by HYDROGEN bonds A binds to T C binds with G • • • Process of DNA copying itself Steps • DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break) • Each side acts as a template • New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules • Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand. Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis) • • • • • Remember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the protein on the ribosome. Made of amino acids DNA mRNA protein DNA RNA PROTEIN • DNA is in nucleus • GENES (made of DNA) hold code for protein • mRNA is made in nucleus • TRANSCRIPTION • Remember base pairing rules • mRNA goes to ribosome • 3 bases on mRNA is a codon – each codon codes for one amino acid • tRNA brings the right amino acid to the mRNA • Anticodon on tRNA base pairs with codon on mRNA 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. DNA mRNA Nucleus Cytoplasm Ribosome Codon Anticodon tRNA Amino acid Protein (polypeptide) • • • Be sure to use mRNA You won’t have to memorize this! What amino acid is coded for by the DNA ATA GAG First convert DNA to mRNA ATA GAG UAU CUC UAU = tyr CUC = Leu