* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 7 CQ
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
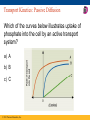
CLICKER QUESTIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Click to edit Master title style Function Click to edit Master subtitle style Questions prepared by Jung Choi Georgia Institute of Technology © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Membrane Structure Which of the following best describes the structure of a biological membrane? a) two layers of phospholipids with proteins embedded between the two layers b) a mixture of covalently linked phospholipids and proteins that determines which solutes can cross the membrane and which cannot c) two layers of phospholipids with proteins either crossing the layers or on the surface of the layers d) a fluid structure in which phospholipids and proteins move freely between sides of the membrane e) two layers of phospholipids (with opposite orientations of the phospholipids in each layer) with each layer covered on the outside with proteins © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Osmosis Which of the following statements about osmosis is correct? a) If a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, more water will enter the cell than leaves the cell. b) Osmotic movement of water into a cell would likely occur if the cell accumulates water from its environment. c) The presence of aquaporins (proteins that form water channels in the membrane) should speed up the process of osmosis. d) If a solution outside the cell is hypertonic compared to the cytoplasm, water will move into the cell by osmosis. e) Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a region of lower water concentration to a region of higher water concentration. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Membrane Lipids and Fluidity An animal cell membrane will be more fluid at room temperature if it contains a) more cholesterol. b) longer chain fatty acids. c) more cis-unsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. d) more trans-unsaturated fatty acids. e) any of the above © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Lipid Rafts, Cholesterol, and Membrane Fluidity Regions of the plasma membrane called “lipid rafts” have high concentrations of cholesterol. Consequently, the proteins in lipid rafts a) diffuse more freely in the membrane. b) tend to stay clustered together. c) are able to flip across the lipid bilayer from inside to outside and vice versa. d) cannot function as receptors. e) cannot undergo endocytosis. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Transmembrane Domains Which of the following amino acids would most likely be present in the transmembrane domain of an integral membrane protein? a) a charged amino acid like lysine b) a polar amino acid like serine c) a special amino acid like glycine or proline d) a hydrophobic amino acid like valine e) any of the above, with no preference © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Membrane Synthesis and Sidedness An oligosaccharide covalently linked to a lipid in the lumen of the rough ER may end up on the a) cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. b) extracellular face of the plasma membrane. c) cytoplasmic face of a secretory vesicle. d) any of the above © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Membrane Permeability Which of the following molecules will diffuse most quickly across a lipid bilayer membrane? a) H2O b) O2 c) H2PO4– d) glucose e) Na+ © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Osmosis If a marine algal cell is suddenly transferred from seawater to freshwater, the algal cell will initially a) lose water and decrease in volume. b) stay the same: neither absorb nor lose water. c) absorb water and increase in volume. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Transport Kinetics: Passive Diffusion Which of the curves below illustrates uptake of nitrous oxide into the cell, if nitrous oxide diffuses passively across the membrane? a) A b) B c) C © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Transport Kinetics: Passive Diffusion Which of the curves below illustrates uptake of lactose into the cell via a passive transporter? a) A b) B c) C © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Transport Kinetics: Passive Diffusion Which of the curves below illustrates uptake of phosphate into the cell by an active transport system? a) A b) B c) C © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.