* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regulation
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
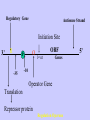
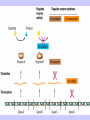
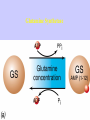
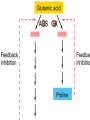
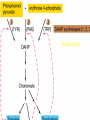
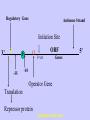
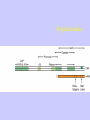
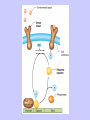
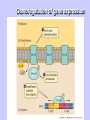
Gene Expression Gene Regulation Regulatory Gene Antisense Strand Initiation Site 3’ R O P -35 ORF 1st nt Genes -10 Operator Gene Translation Repressor protein Regulation Operons 5’ Gene Regulation Genes Encode Functions NOT Always Required E. coli in Glucose Medium containing Amino Acids No Need for Enzymes to Alternate C Lactose No Need to Synthesis Amino Acids Regulation Needs Nutritional Environment Physical Environment Signals that facility Transcription ‘+” Signals that interfere with Transcription “-” Regulation Occurs at Any Level Transcription* - Binding RNA Polymerase at P site mRNA - amount of Turn over Alter Sigma’s “Strength of P” Translation Step Enzyme Function- Repressor or Reduction General Features of Regulation Constitutive: Expressed All Time Gene Switch always on Enzymes and Structural Adaptive or Inducible Only if Needed Regulation Specific Controlling one gene or Operon Global Controlling Wide Range Nutritional or Physical Anaerobic Respiration Heat Shock Osmotic Stress Major Modes of Regulation Activity of Preexisting Enzymes: Posttranslational Course Control Rapid-Seconds Amount of Enzymes: Transcription Slow in terms of Minutes New Enzyme Synthesis Dilution of Existing Enzymes Inhibiting Enzyme Activity Posttranslational Some Enzymes Need Processing for Activity Most Enzymes Synthesized With Full Activity Therefore Need specific Cell Inhibitors Feed Back Inhibition Final Product of Biosynthetic Pathways Block The 1st Enzyme in the Reaction Assimilation of ammonia Modification of Enzymes Glutamine Synthetase Glutamine Synthetase HOW? Feed back Works Allostery Active Site: substrate Binds Allosteric Site: the Inhibitor or “ Effector” Binds Isoenzymes Regulation of Transcription Control of Amount of Protein Switch “ON” All Time unless “Off” repressor Protein P Site on Operon Very Close to Consensus Consequence Shine-Dalgarno Complimentary to 16S rRNA More gene Transcribed More the Amount Regulatory Gene Antisense Strand Initiation Site 3’ R O P -35 ORF 1st nt Genes -10 Operator Gene Translation Repressor protein Regulation Operons 5’ Negative Control of Transcription Switch is always on: Needs a repressor protein to cut off Two ways to happen: Enzyme Repression ; Ex. AA Arginine is Synthesized if: NO Arginine present in medium Enzyme Reduction: The Synthesis of an Enzyme ONLY if Substrate is present Terms Bacteria Adapt to Specific Conditions By altering levels of mRNA Constitutively- is without Control only Strength of Promoter Adaptive – Ability to initiate Transcription –Control by signal Proteins Environmental Signals facilitate Transcription Positive Regulation Environmental Signals interfere with Transcription Negative Regulation Negative Regulation Terms: Inducer: Substance Initiates Enzyme Induction Co repressor: Represses Production Collectively Called Effectors (small molecules) Negative Regulation Enzyme Reduction LAC Operon: No Lactose Present-Repressor binds to Operator Near Promoter- NO Transcription Lactose Present: Repressor & Inducers (allolactose) bind to Prevent binding repressor Positive Regulation Signaling Proteins Activator Proteins Not Repressor Together Stimulate Transcription Tryptophan Maltose Catabolite Activation Lactose present Low Glucose (Note: Glucose Inhibits CAMP) cAMP Complex with Catabolite Activator Protein CAP Together they bind to polymerase to Activate Transcription Diauxic growth b-galactosidase Catabolite Activator Protein CAP cAMP B-galactosidase TWO COMPONENT Regular System Sensor Kinase: Phosphorylases its’ self in response to environmental Signal Response Regulator: Acts as Repressor Osmoregulation of gene expression