* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen?
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
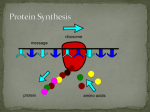
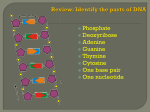
DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen? Problem? How do we go from DNA to individual traits? DNA acts as a blueprint • DNA acts as a blueprint for making proteins • It is these proteins that give you your hair and eye color! Gee- what do ribosomes do? • • • • Make Proteins Where are they? Cytoplasm & RER DNA- the “recipe” for making proteins is located in the nucleus • HOW DO WE GET FROM NUCLEUS TO CYTOPLASM? DNA to RNA? • The instructions for assembling proteins are “transferred” from DNA to RNA, which is the second type of nucleic acid. DNA vs. RNA • Single Chain of nucleotides • Sugar is Ribose • Uracil instead of thymine –Complimentary to adenine Transcription • Transferring information from DNA to RNA is called transcription • Same as replication, except Adenine will pair with Uracil –Fill in the strand RNA Does the GRUNT WORK! • After TranscriptionRNA goes to the cytoplasm to find a Ribosome to make proteins • 3 types of RNA to do this work!! • mRNA • tRNA • rRNA THE RNA’s • mRNA (messenger) – Carries transcribed DNA code to ribosome • tRNA (transfer) – Brings amino acids to ribosome in correct order • rRNA – w/ other proteins makes up structure of ribosome CHECKPOINT- Fill it in!!!! DNA • Double Helix • Adenine • Guanine • Cytosine • Thymine • Deoxyribose RNA • Single Strand • Adenine • Guanine • Cytosine • Uracil • Ribose CHECKPOINT 2 • mRNA • tRNA • rRNA • Carries transcribed DNA code to ribosome • Brings amino acids to the Ribosome • Assists in ribosome structure FINALLY! RNA to Proteins First, ya gotta understand how the genetic code works! Humans vs. Hard Drives • DNA stores info in the form of long sequences of bases • 30,000 genes in humans –3 billion base pairs • Base pairs make up code for amino acid sequence, which make up the protein. •A 3 base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. Each codon translates to a particular amino acid. •20 amino acids make up all proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. These Codons are used by all living things; thus, showing the unity of life on Earth Protein Synthesis • 1) TranscriptionDNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus • 2) mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome Protein Synthesis (continued) • 3) Translation- the ribosome reads the codon and matches it with its anticodon carried by the tRNA’s in the cytoplasm. Attached to these anticodons are the amino acids that will be built into a protein Protein Synthesis (continued) • 4) ElongationRibosome will continue to build proteins one amino acid at a time. During this time, tRNAs continue to bring the corresponding amino acids until ribosome enters a “STOP” codon. – Ribosome falls off mRNA and protein ready for use Now…Let’s practice