* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
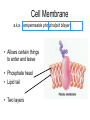
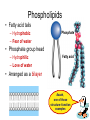
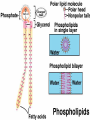
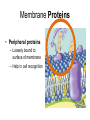
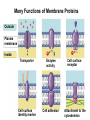
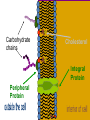
The Plasma Membrane Where are membranes found? • Cell • Organelles Review • Selectively permeable – Allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. • Purpose – Cells must keep the proper concentration of nutrients and water and eliminate wastes. Cell Membrane a.k.a. semipermeable phospholipid bilayer • Allows certain things to enter and leave • Phosphate head • Lipid tail • Two layers Phospholipids • Fatty acid tails – Hydrophobic – Fear of water Phosphate • Phosphate group head – Hydrophilic – Love of water Fatty acid • Arranged as a bilayer Aaaah, one of those structure–function examples Phospholipid bilayer polar hydrophilic heads nonpolar hydrophobic tails polar hydrophilic heads Membrane fat composition varies • Fat composition affects flexibility – Membrane must be fluid & flexible • Cholesterol! – Adds structure and flexibility More than lipids… • In 1972, S.J. Singer & G. Nicolson proposed that membrane proteins are inserted into the phospholipid bilayer It’s like a fluid… It’s like a mosaic… It’s the Fluid Mosaic Model! Membrane Proteins • Help determine what particles can pass through the membrane. – Act as channels and pumps Membrane Proteins • Peripheral proteins – Loosely bound to surface of membrane – Help in cell recognition Membrane Proteins • Integral proteins • A.k.a. transmembrane protein – Penetrate lipid bilayer – Usually across whole membrane – Transport proteins • Channels and pumps Many Functions of Membrane Proteins Outside Plasma membrane Inside Transporter Enzyme activity Cell surface receptor Cell surface identity marker Cell adhesion Attachment to the cytoskeleton Membrane Carbohydrates • Play a key role in cell-cell recognition – Ability of a cell to distinguish one cell from another – Important in organ & tissue development • Glycolipid • Glycoprotein Review • Phospholipid bilayer – Two Layers – Phosphate head – Lipid tail • http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life /memb.htm Carbohydrate chains Cholesterol Integral Protein Peripheral Protein Any Questions??