* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIPID METABOLISM - Orange Coast College
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Cryobiology wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
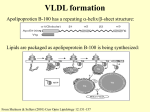
LIPID METABOLISM I. Lipid Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Triglycerides ~ 90% of dietary lipids Metabolic NRG storage Oxidized to CO2 and H2O Triglyerides, cont… oxidation state than glucose metabolism of fats yields ~9 kcal/gram vs ~4 kcal/gm Carbohydrates, proteins Triglyceride Storage, cont… Stored in anhydrous state Non-polar Provide ~ 6 times energy of hydrated glycogen Triglyceride storage, cont… Stored in large quantities in cells Non-reactive with other cell components Segregated into lipid droplets Do not affect osmolarity of cytosol Triglycerides, cont… To be used as fuel: insoluble in H2O Must emulsify before lipid digestion in intestine Must be “carried” in blood (proteins) Triglycerides, cont… Sources of fat Three cellular sources Fat in diet Fat stored in cells Fat synthesized in one organ and transported to another Triglycerides, cont… Fats obtained vary by organism Vertebrates Fat in diet Fat in adipose tissue Convert excess carbohydrate to fat in liver for export Triglycerides, cont… Humans Industrialized countries: ~ 40% of daily calorie consumption is fat Should be < 30%! Atkins kills… Humans, Triglycerides, cont… Used for > half the energy in: Liver Heart Resting skeletal muscle Humans, Triglycerides, cont… Hibernating animals and migrating birds sole source of NRG Higher plants: Do not depend on fats for energy Germinating seeds Lipid digestion, cont… Digestion Triglyceride digestion takes place at lipid-water interfaces Rate is based on surface area at interfaces Peristalsis Emulsification by bile Lipid digestion, cont… Bile Synthesized from cholesterol, biliverdin By liver Stored in gallbladder Released after ingestion of fat Lipid digestion, Bile, cont… Acts as digestive detergent Converts dietary fats into mixed micelles Micelles contain bile salts and triglycerides Lipid digestion, cont… Role of lipase Pancreatic lipase: catalyzes hydrolysis of triglycerides At 1 and 3 positions sequentially Forms 1,2-diglycerol 2-glycerol Soap Role of lipase, Lipid digestion, cont… Phospholipase A: Pancreatic enzyme Degrades phospholipids Hydrolysis at C(2) Absorption of Lipids Absorption Molecules diffuse into cells of intestine Facilitated by bile salts Micelles transport non-polar lipids across aqueous boundary layer Absorption, cont… Bile salts essential Fatty Acids Fat soluble vitamins A,D,E & K Biliary disease interferes Lipid Uptake in Vertebrates Role of Lipase, cont… Reconversion: in mucosa cells Lipid digestive products triglycerides Packaged into Chylomicrons Lipoprotein aggregates Triglycerides, cholesterol, protein Chylomicron Aggregate of triglycerides, cholesterol, and proteins Reconversion, Role of Lipase, cont… Released into bloodstream: Via lymphatic system Lacteals Triglycerides synthesized in liver Packaged in VLDL Directly released into blood Role of lipase, cont… Transport APOLIPOPROTEINS: lipid-binding blood proteins Transport between organs Form classes based on density Role of lipase, cont… Proteins on outside of Chylomicron Are apoproteins Act as cell surface receptors for recognition (apo C-II) Lipid Uptake in Vertebrates Transport, Role Chylomicrons, cont… Chylomicrons and VLDL: Move triglycerides, cholesterol To Skeletal muscle & adipose LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE an extracellular enzyme Activated by apo C II Hydrolyzes triglycerides Chylomicron Carry triglycerides, cholesterol to tissues via lymphatic system (lacteals) Transport, Role of lipase, cont… Deletes lipoprotein from triglyceride LDL: (130-159 mg/dl) Forms IDL Then LDL removed from plasma at liver, adrenals, adipose HDL: (above 35 mg/dl) moves cholesterol from tissues Sends to liver for excretion in bile salts Ratio LDL:HDL = 2:1 Lipid Metabolism, cont… Uptake by cells FA taken in by: muscle: oxidized for NRG adipose: stored as triglyceride Lipid Uptake in Vertebrates Transport, Role of lipase, cont… Glycerol Transported to liver or kidney Converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate And then??? Pathway to Glycolosis Conversion of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone phosphate Transport, Role of lipase, cont… Remnants of Chylomicrons triglycerides; cholesterol and apoproteins (apo E, apo B-48) To liver Uptake by endocytosis Triggered by apolipoproteins Uptake in Liver via Endocytosis Chylomicron Remnants, cont… Triglycerides Oxidized for energy or Converted to ketone bodies Excess fatty acid Convert to triglycerides Pack into VLDL To adipose for storage Lipid Uptake in Vertebrates Mobilization of Stored Fats Mobilization of stored triglycerides Triggered by hormones Stimulus is in blood glucose Hormones: Epinephrine Glucagon Mobilization of Stored Fats, Hormone Action, cont… Activate adenylate cyclase in adipocyte plasma membrane Increases cAMP Activates protein kinase Activates triglycerol lipase Catalyzes hydrolysis of ester bonds in triglycerides Mobilization of Stored Fats Action of second messenger hormones triggers mobilization of stored triglycerides Role of lipase, cont… Free fatty acid released into bloodstream Binds to serum albumin Carried to tissues Released to diffuse into cells Role of lipase, cont… NOTE: Glycerol glycerol-3-phosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate glycolysis II. Fatty Acid Oxidation FA activation: Free FA cannot enter Mitochondria Occurs in cytosol Acyl-CoA synthetases (thiokinases) 3 isozymes mitochondrial membrane FA activation, cont... FA + CoA + ATP fatty acyl-CoA + AMP + PPi different acyl-CoA’s work on different FA Fatty acyl-CoA: high energy compound Fatty acid oxidation, cont… Transport across mitochondrial membrane: Formation of fatty acyl-carnitine Carnitine acyl transferase I Outer face of inner membrane Fatty acyl from CoA carnitine CoA released cytoplasm Transport across mitochondrial membrane, cont… Acyl-carnitine/carnitine transporter Carrier Fatty acyl-carnitine matrix carnitine to inter-membrane space Facilitated diffusion F.A. Entry into Mitochondria Fatty acid oxidation, cont… Transfer of acyl from Carnitine to intra-mitochondrial membrane Carnitine acyltransferase II Inner face of inner membrane Regenerates fatty acyl-CoA Frees carnitine returns to cytosol Carnitine Acyltransferase II, cont… Two separate pools of CoA (ATP, NAD+) Cytoplasm: makes FA Mitochondria: oxidative degradation Pyruvate FA AA ß-oxidation ß-oxidation: FA dismembered to fatty acyl-CoA Mitochondrial oxidation of FA Stage One: ß-oxidation Remove 2-C chunks as acetyl-CoA Begins at carboxyl end of fatty acid chain ß-Oxidation Fatty acids are dismembered into Acetyl-CoA subunits Each acetyl Co-A sends 4 H to NAD, FAD Mitochondrial oxidation, cont… For example, 16C palmitic acid 8 acetyl CoA Stage Two: oxidation of acetyl-CoA CO2 Stage Three: oxidative phosphorylation ATP (+H2O) ß oxidation, cont… ß oxidation: 4 reactions Formation of a trans – a, ß double bond Between C-2 (a) and C-3 (ß) 2 Yields: Trans-∆ -enoyl-CoA Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase FAD 2 ATP Similar to succinate dehydration ß-Oxidation First: formation of double bond Second: hydration of double bond Third: dehydrogenation Fourth: cleavage to Acetyl Co-A ß-oxidation, cont… Hydration of the double bond By enoyl-CoA hydrase Forms 3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA Similar to fumarase reaction ß-oxidation, cont… Dehydrogenation By ß-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase To ß-ketoacyl-CoA NAD 3 ATP Similar to malate dehydrogenase reaction ß-oxidation, cont… Ca -Cß cleavage (thiolysis) Catalyzed by ß-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (thiolase) Produces: acetyl-CoA fatty acyl-CoA (2 carbons short) ß oxidation: Enzymes in Mitochondrial membranes 3 kinds of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase Specify short, medium, long chain fatty acid Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) Deficient in ~10% of SIDS babies More common than PKU Sites of Mitochondrial Enzymes ß-oxidation, cont… Fatty acid oxidation is highly exergonic Each round of ß-oxidation 1 NADH 1 FADH2 1 acetyl-CoA ß-oxidation, Energy Payoff Acetyl-CoA citric acid cycle Example: PALMITOYL-CoA (16C) 7 rounds of ß -oxidation 7 NADH 7 FADH2 8 acetyl CoA So, 7 + 24 NADH = 31 x 3 = 93 ATP 7 + 8 FADH2 = 15 x 2 = 30 ATP + 8 GTP 131 hi-energy molecules for fatty acyl CoA - 2 ATP 129 total ß-oxidation, cont… READ IN TEXT: Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acid: 2 additional reactions Oxidation of odd-chain fatty acid: 3 additional reactions III. Ketone Bodies Acetyl-CoA from ß-oxidation Enters citric acid cycle Converted to KETONE BODIES Water-soluble “equivalent” of FA Ketone bodies, cont… Ketogenesis Occurs in liver: acetyl CoA ketone bodies Primary ketone bodies Acetoacetate - out of liver D-ß-hydroxybutyrate - out of liver Acetone - exhaled Ketone Body Formation Ketone bodies, cont… Function: fuel for peripheral tissues Heart, skeletal muscle Brain Normal fuel is glucose In starvation: ketone bodies Enzyme production adapts over time >40 days, provide 70% energy Ketone bodies, cont… Production and transportation Determined by availability of oxaloacetate Combine with acetyl group enter TCA cycle Ketone bodies, cont… In starvation Oxaloacetate pulled from citric acid cycle Used in gluconeogenesis [oxaloacetate] decreases therefore little kreb’s cycle Production of ketone bodies is favored Production and transportation, cont… Overproduction: starvation, diabetes Moved from liver to other tissues Allows fatty acid oxidation in liver In tissues: ketone bodies converted back to acetyl-CoA Production and transportation, cont… Formation of ketone bodies from acetyl-CoA occurs in the mitochondrial matrix thiolase 2 Acetyl-CoA acetoacetyl-CoA Acetoacetyl-CoA + acetyl-CoA ß -hydroxy- ß -methylglutaryl-CoA HMG-CoA free acetoacetate + acetyl-CoA Production and transportation, cont… Acetoacetate D- ß -hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase D-ß-hydroxybutyrate Acetoacetate decarboxylase Acetone High in uncontrolled diabetes Production and transportation, cont… Ketosis Pathological Acetoacetate produced too fast for elimination Breath smells like acetone Blood pH decreases acidosis Lipid Biosynthesis “Reverse” of lipid catabolism Know differences Where in the cell does each occur? What are the e- transport molecules? What are the acyl group carriers? Where does acetyl Co-A “fit into” each set of reactions? Pathway Differences Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Read in Text For major steps, know Type of reaction Enzyme Product Cholesterol Biosynthesis Read in Text Know Draw steps Intermediates