* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
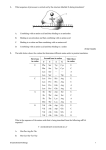
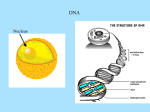
Using This Program-Protein Synthesis This program works with simulation kit: Protein Synthesis made by “”, and modified by Holomuzki and Bradley. As you read a slide, you may come across a word in a different color. Click on that word with the mouse and it will take you to another slide. Try it! When you finish with a slide, simply click the mouse to move to the next slide. Using This Program-Protein Synthesis That’s all there is to it. When you get to the end, just right click or click on the arrow here, and then click on ‘End Show’, If you don’t see the arrow, move the mouse and it will appear! Protein Synthesis This process uses information coded in huge DNA molecules, transfers that information to smaller RNA molecules, then assembles the proteins from amino acids. All that makes sense if you know what DNA and RNA are. I want to do the review. Do Review I want to skip the review. Skip Review DNA & RNA Both of these are Nucleic Acids. Both are made of Nucleotides that contain P a phosphate S a sugar B a base that contains nitrogen in this shape: B p S Nucleotides form Chains They can be single chains. 1 Or double chains 1 2 RNA has bases: Adenine Uracil single stranded Guanine Cytosine Ribose is its sugar DNA has bases: Adenine Thymine double stranded Guanine Cytosine Deoxyribose for sugar DNA & RNA How are DNA and RNA similar? How are DNA and RNA different? Base Pair Bonding--DNA/RNA In both of these molecules, the bases bond in very specific ways. In both, Guanine and Cytosine always bond with each other and not with anything else. In DNA Adenine and Thymine always bond with each other and not with anything else. In RNA Adenine and Uracil always bond with each other and not with anything else. Bonding Between DNA & RNA When an RNA is made from DNA, the DNA bases and the RNA bases bond. If the DNA base is Guanine, RNA Cytosine bonds to it and vice versa. If the DNA base is Thymine, RNA Adenine bonds to it. BUT if the DNA base is Adenine, RNA Uracil will bond to it. DNA & RNA Remember the differences and similarities. Number of strands/type of sugar/bases Remember how their bases bond to one another. G to C and C to G A to T and T to A (DNA only) A to U and U to A (RNA only) A (DNA) to U (RNA) Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis is the cellular process used to make proteins. Synthesis just means the building up. The DNA contains the directions for making LOTS of proteins. When a specific protein is needed only the part of the DNA that contains those specific directions is used. Three different types of RNA are used in making a protein. Protein Synthesis -- Two Parts Transcription is the first part of Protein Synthesis. It occurs in the nucleus. It transfers information from the huge DNA molecule to a much smaller RNA molecule. Translation is the second part. It occurs in the cytoplasm. It involves three types of RNA and uses those three to make a protein out of amino acids. Three Types of RNA: mRNA Messenger RNA also called mRNA. Has a straight line shape. Contains the directions for the protein from the DNA. Those directions are in three base groups called codons. mRNA: Codons The language of RNA is made up of three letter words and the alphabet contains only four letters, the four bases A U G C. Each of these codons or “words” represents a different amino acid. Codon 1 Codon 2 mRNA: Codons to Amino Acids Use this table to figure out what amino acid is coded for by UCA. UCA = ser I don’t see how you found ser, help! Go to abbreviation/ Amino Acid name. First Base U C A G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly mRNA: Codons to Amino Acids Here is the table again. What does UAU code for? What does AGC code for? Go to abbreviation listing. First Base U C A G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly mRNA: Codons to Amino Acids Do different codons ever code for the same amino acid? First Base U C A G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly mRNA So that is basically mRNA. Remember these important points: mRNA is made from DNA. mRNA carries directions from DNA to the ribosome. The code is carried by 3 base “words” called codons. Codons code for specific Amino Acids. Three Types of RNA: rRNA Ribosomal RNA also called rRNA Occurs in two parts that fit together. Forms the ribosome. Is the site for protein synthesis. Three Types of RNA: t-RNA Transfer RNA, also called tRNA. Folds back on itself Carries an Amino Acid to the ribosome. Has an anticodon at one end. Amino Acid Transfer RNA The tRNA anticodon will bind with a specific mRNA codon. Anticodon ACG bonds with codon UGC. ACG can only carry the amino acid Cysteine, coded for by UGC. Transfer RNA Because tRNA has such a complex shape, we will be using the substitute shape shown. The amino acid still binds to the top and the anticodon is still at the bottom. A G A tRNA with Amino Acid This is the tRNA with its Amino Acid attached and the appropriate anticodon. Why doesn’t the anticodon match with the Amino Acid Chart? Serine tRNA A G A Using This Program-Protein Synthesis So now you are on a different slide. To get back to where you were, simply click on the Return to Lesson below. (Wait for the starburst to stop.) Return to Lesson DNA/RNA Similarities Both are nucleic acids, made of nucleotides. Both contain a sugar, phosphate, and bases The phosphate in each is the same. Of the bases these are used in both. Guanine Cytosine Adenine Show me a picture of each. Return to Lesson Codons: UCA = Serine (1) Locate U in this column/Locate C in this row/Find UCA in the box U U UUU UUC UUA AAC C UCU UCC UCA UCG A UAU UAC UGA UAG G UGU UGC UGA UGG C CUU CUC CUA CUG CCU CCC CCA CCG CAU CAC CAA CGA CGU CGC CGA CGG Codons: UCA = Serine (2) Now you have found UCA on the chart. Your chart may have the name of the amino acid written next to the codon “Serine” Or it may have an abbreviation “ser”. If the abbreviation is there, then look that up in the listing of amino acids. “serine” That is the name of the amino acid. Return to Lesson DNA/RNA Pictures RNA DNA Return to Lesson DNA/RNA Differences RNA is single stranded, DNA is double. RNA has ribose as the sugar, DNA has deoxyribose. RNA has Uracil as a base, DNA has Thymine. Show me a picture of each. Return to Lesson mRNA: Codons to Amino Acids Look up the abbreviation in this list to find the name of the amino acid coded for by any of the abbreviations. ala arg aspg aspt cys glun glut gly his iso alanine arginine asparagine aspartate cysteine glutamine glutamate glycine histidine isoleucine Return to Lesson leu lys met phe pro ser thr try tyr val leucine lysine methionine phenylalanine proline serine threonine tryptophan tyrosine valine UAU Codons Tyrosine First Base U C A Return to Lesson G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly AGC Codons Serine First Base U C A Return to Lesson G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly Codons Do different codons ever code for the same amino acid? First Base U C YES! UCA, AGC and others are Serine Return to Lesson A G Second Base U C A UUU phe UCU ser UAU tyr UUC phe UCC ser UAC tyr UUA leu UCA ser UAA stop UUG leu UCG ser UAG stop CUU leu CCU pro CAU his CUC leu CCC pro CAC his CUA leu CCA pro CAA glun CUG leu CCG pro CAG glun AUU iso ACU thr AAU aspg AUC iso ACC thr AAC aspg AUA iso ACA thr AAA lys AUG met * ACG thr AAG lys GUU val GCU ala GAU aspt GUC val GCC ala GAC aspt GUA val GCA ala GAA glut GUG val GCG ala GAG glut G UGU cys UGC cys UGA stop UGG try CGU arg CGC arg CGA arg CGG arg AGU ser AGC ser AGA arg AGG arg GGU gly GGC gly GGA gly GGG gly tRNA with Amino Acid Why doesn’t this match with the Amino Acid Chart? Remember the Amino Acid Chart is set up based on CODONS, not ANTIcodons. The Codon that would bind to AGA is UCU, and UCU codes for Serine. So this tRNA is correct. Return to Lesson