* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Anatomy
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
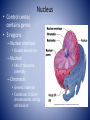
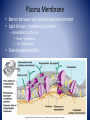
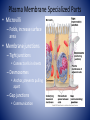
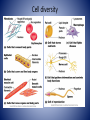
Cell Anatomy Cell • Basic unit of living organisms • ~60% water • Bathed in interstitial fluid (external) • Vary in shape and function • 3 main regions – Nucleus, plasma membrane, cytoplasm • Control center, contains genes • 3 regions Nucleus – Nuclear envelope • Double membrane – Nucleoli • Site of ribosome assembly – Chromatin • Genetic material • Condenses to form chromosomes during cell division Plasma Membrane • Barrier between cell contents and environment • Lipid bi-layer, cholesterol, proteins – Assembled tail to tail • Head – hydrophilic • Tail- hydrophobic • Selective permeability Plasma Membrane Specialized Parts • Microvilli – Folds, increase surface area • Membrane junctions – Tight junctions • Connect cells in sheets – Desmosomes • Anchor, prevents pulling apart – Gap junctions • Communication Cytoplasm • Internal cellular material • Contains three elements – Cytosol • Fluid that suspends the other elements – Inclusions • Stored products/nutrients – Organelles • Metabolic machinery Cell Organelles • Mitochondria – site of ATP generation • Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis • Endoplasmic reticulum – fluid filed tubules – Rough ER – studded with ribosomes – Smooth ER – lipid metabolism, detoxification • Golgi apparatus- flattened stack of sacs, modifies and packages • Lysosomes – cell demolition site • Peroxisomes – detoxifies poisons and reactive chemicals Cell Organelles • Cytoskeleton - Internal framework – Composed of • Intermediate filaments – resist forces • Microfilaments – cell motility, shape changes • Microtubules – determine shape, organelle distribution • Cell projections – Cillia – hair like appendages – Flagella – long projections, motility Cell diversity • Over 200 types in the human body • All vary in shape and function • Specialized – Connect – Cover – Move – Storage – Fight disease – Control/information gathering – Reproductive Cell diversity