* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “cells”. - Biggs` Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
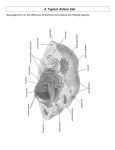
The Cell AP Biology Chapter 6 AP Bio Big Ideas • Big Idea 4: Biological Systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties – Essential Knowledge 4.A. 2- the structure and function of subcellular components, and their interactions, provide essential cellular processes. Why is life cellular? • Because every living thing is made up of cells. The Immortal cells of Henrietta Lacks- HeLa Cells. Van Leeuwenhoek • Anton van Leeuwenhoek one of the first people to see living things in a drop of pond water. Robert Hooke • Observed tiny chambers in plants. Called them “cells”. The Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • New cells come from existing cells. Basic Cell Structures • All cells have a cell membrane and cytoplasm. Plant and some bacteria have cell walls. • Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann concluded that all plant and animals were made of cells. Limits to cell size • A high ratio of surface area to volume is important for cells – Exchange of material with surroundings is easier with a large surface area and smaller volume. – Elephants don’t have larger cells they have more cells. The cell membrane is a fluid “mosiac” bilayer . The cell membrane is semipermeable, it regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote • Scientist divide cells into two categories –Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. –The domains Bacteria and Archaea are prokayotes. –The domain Eukarya are eukaryotes. Prokaryote cells • Smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells • Do not contain a nucleus • Have no organelles • All bacteria are prokaryotes. Eukaryote Cells • Larger than prokaryotic cells. • Contain a nucleus • Have organelles that carry out special functions. Prokaryote •Cell membrane •Cytoplasm Eukaryote •Cell membrane •Cytoplasm •Have no nuclei •Have nuclei •Have no organelles •Have organelles •All bacteria are prokaryotes •Can be single- celled or multicellular organisms •Includes plants, animals, fungi, & protists The Eukaryotic Cell • Extensive and elaborate internal membranes – Divide cell into compartments – Participate in cellular metabolism – Allow incompatible processes to occur simultaneously. Nucleus • Controls most cell processes • Contains hereditary information (DNA) • Directs protein synthesis by synthesizing RNA. • Chromatin–the granular material in the nucleus – –made of DNA and protein • Chromatin is separated into units called chromosomes. Nucleolus • Small dark area in an undividing nucleus • rRNARibosomes are synthesized into large and small subunits. • Some species may have 2 or more nucleoli. Nuclear Envelope • Surrounds the nucleus • Double-membrane dotted with nuclear pores • RNA and other molecules are sent out of the nucleus Ribosomes • Small particles of RNA • Make proteins following coded instructions (mRNA) from the nucleus. • Free ribosomes in the cytosol • Bound ribosomes attached to the ER. Endomembrane System • Some of the different membranes in the cell are part of endomembrane system. • Related through direct contact or vesicles • Includes – nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, some vacuoles and the plasma membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum continuous with nuclear envelope 2 types • Rough ER – Ribosomes attached – Modifies proteins into native conformation – Attaches carbohydrates to proteins – glycoproteins – Secretory proteins are wrapped in transport vesicles • Smooth ER – Lacks ribosomes – Synthesizes lipids – Metabolism of carbohydrates – Detoxification of drugs and poisons. – Stores Ca ions (i.e. muscle cell contractions) Golgi Apparatus • Protein modification • Proteins are stored and shipped to other destinations • Manufactures some macromolecules Lysosomes • Filled with hydrolytic enzymes • Break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods for cell use. Vacuoles • Stores water, salts, proteins, or carbohydrates • Provide pressure for plants cells • Include contractile vacuoles and central vacuole. Mitochondria & Chloroplasts • Enclosed by membranes, but not part of endomembrane system • Two membranes • Semi autonomous organelles – grow and reproduce in the cell • Contain their own DNA – synthesize proteins made on their ribosomes. Mitochondria • Site of cellular respiration – production of ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels with the help of O2 • Folded inner membrane provides large surface area for proteins that function in respiration. Chloroplasts • Specialized member of plastids family • Site of photosynthesis • Plants and some other type of organisms are able to use light energy from the sun to produce food. Photosynthesis • Uses the energy of sunlight to change water and carbon dioxide (CO2) into oxygen (O2) and high energy sugar. • Inside the chloroplast are thylakoid membranes. A granum is a stack of thylakoids. The light dependent reactions happen in the thylakoid. Peroxisomes • Metabolic compartment that contain enzymes that transfer H from various substrates to O to produce H2O2 • Some use O to break down fatty acids into smaller molecules for transport to mitochondria. • Do not bud from endomembrane system but increase by splitting in two. Microfilaments • Network of protein filaments • Maintain the cell shape-Cytoskeleton • Centrioles in animal cells • Use for many forms of cell movement Cell Wall • Extracellular structure • Found in plants & algae. • Provides support and protection • Made of cellulose, a tough carbohydrate fiber. • Perforated by channels called plasmodesmata, between cells.