* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A View of the Cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
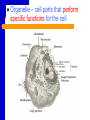
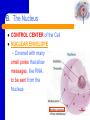
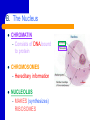
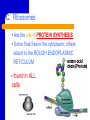
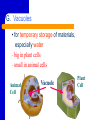
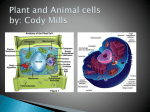
Cell Organelles “Tiny organs” of the Cell Objective: C2 - Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell and compare the structures of plant, animal, & bacteria cells recognizing their complexity – cell parts that perform specific functions for the cell Organelle A. Cytoplasm Everything between the cell membrane and the nucleus A jellylike mixture that consists mostly of water B. The Nucleus CONTROL CENTER of the Cell NUCLEAR ENVELOPE – Covered with many small pores that allow messages, like RNA, to be sent from the Nucleus B. The Nucleus CHROMATIN – Consists of DNA bound to protein CHROMOSOMES – Hereditary information NUCLEOLUS – MAKES (synthesizes) RIBOSOMES C. Ribosomes • Are the site of PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • Some float free in the cytoplasm; others attach to the ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • found in ALL cells D. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • the site where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled • is primarily a transportation system • ROUGH - has ribosomes • SMOOTH - no ribosomes E. Golgi Apparatus/Body • Processing, Packaging, and Secretion • System of membranes made of flattened sac like structures F. Lysosomes • Filled with enzymes • Digestion of macromolecules (lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins) into molecules that can be used by the cell • Involved in breaking down old cell parts (Not found in plant cells) G. Vacuoles • for temporary storage of materials, especially water - big in plant cells - small in animal cells Animal Cell Vacuole Plant Cell H. Mitochondria • Converts chemical energy stored in food into compounds that the cell can use •"POWERHOUSE" OF THE CELL - ATP is the ENERGY molecule of the cell - ATP is produced in a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION I. Chloroplast CHLOROPLASTS • Capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called Photosynthesis • Not found in animal cells J. Cytoskeleton • Helps maintain cell shape • Helps the cell move • Consists of TWO Types of structures: - MICROFILAMENTS (threadlike) - MICROTUBULES (hollow) K. Centrioles - cylindrical structures that are composed of groupings of microtubules - function in cell division (Not found in plant cells) L. CILIA AND FLAGELLA • Extend from the surface of the cell • Assist in movement • CILIA are short hair like projections (not in plants) • FLAGELLA are long whip like projections Etymology Cytoplasm: cyto-, (cell) + -plasm (to mold) Chloroplast: chloro- (Gk. KHLOROS, greenish yellow) + -plast (to mold) Endoplasmic: endo- (in) + -plasmic (to mold) Lysosome: lyso- (loosening or dissolving) + -some (Gk. SOMA, body) Flagellum: (L. FLAGELLUM, little whip) Cilia: (L. CILIUM, eyelid) NOTE: Cilia reminded scientists of eyelashes. Vacuole: (L. VACUUS, empty)