* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion/Osmosis
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
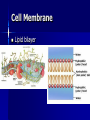
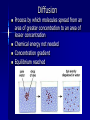
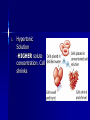
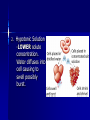
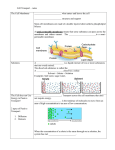
Passive Transport Standard/Obj Know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. Why do vegetables wilt? Homeostasis biological balance between a cell or an organism and its environment Cell Membrane Lipid bilayer 1. 2. Passive Transport-movement of any substance across a membrane w/o use of chemical energy Facilitated Diffusion: transport proteins help move materials across cell membrane Gated Channel: protein controlled opening (channel), some are permanently open Diffusion Process by which molecules spread from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration Chemical energy not needed Concentration gradient Equilibrium reached Osmosis Process by which water molecules diffuse through a membrane from an area of high concen. to area of low concen. 1. Hypertonic Solution -HIGHER solute concentration. Cell shrinks 2. Hypotonic Solution -LOWER solute concentration. Water diffuses into cell causing to swell possibly burst. 3. Isotonic Solution -concen. of water inside and outside the cell are equal (solute concen. are equal) -equilibrium Turgor Pressurewater pressure in cell ex. water pressure forces cytoplasm and cell membrane against the cell wall in plants 1. Plasmolysis-shrinking of a cell from low turgor pressure (hyper) 2. Cytolysis-cell takes in so much water that it bursts (hypo)