* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelles
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
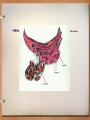
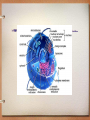
Organelles Little organs of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum • E.R. is a complex system of membranes. • These membranes help to transport materials around in the cell. • Acts like a highway system. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Membranes do NOT have ribosomes attached to them. Smooth E.R. membranes are where * synthesis of lipids * steroids are produced (gland cells) * toxic substances (alcohol) are broken down (liver cells) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes attached to the membranes give a “rough” appearance • Proteins are produced on the ribosomes and then transferred through the rough e.r. membranes Golgi Apparatus • Series of membranes that aid in – 1. processing – 2. modifying – 3. packaging and secreting (exporting proteins) Lysosomes • Small spherical (round) organelles that store strong hydrolytic (acidic) enzymes. • Lysosomes are common in animals, protists and fungal cells. • Enzymes can digest (breakdown): a. Bacteria, viruses, sugars, proteins, and old worn out cell parts. Vacuoles: Plants • Plants: Large central vacuole • Takes up the majority of the space in the plant cell. – Stores large quantities of water – Stores metabolic waste products – Stores enzymes Nucleolus • Spherical area inside the nucleus where ribosomes are produced Flagella • Structure on cell that helps in movement • Whip-like structure