* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
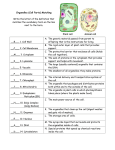
Download Click on each organelle to learn its function
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Click on each organelle to learn its function Cell Membrane • The cell membrane controls passage of substances in and out of the cell. • It is responsible for communication between cells. Chloroplast • The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis in plants. • It is only found in plant cells. Endoplasmic reticulum • There are two types: smooth and rough. • The rough ER is responsible for modifying proteins by folding them into their correct three dimensional shape and preparing them for export. • The smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxifying harmful chemicals. Golgi appartus • Post office of cell • The Golgi apparatus sorts, modifies, and packages molecules including proteins for export from the cell. Lysosome • Contains digestive enzymes and is responsible for digesting waste and bacteria in the cell. Mitochondria • Site of the Kreb’s cycle and electron transport system in cellular respiration. • Known as “powerhouse of the cell” Nucleus • Contains cell’s DNA. • Control center of cell Ribosome • Site of protein synthesis. It makes the amino acid chains which are sent to the rough ER to be folded. Vacuole • Responsible for storage in cells. Cell Wall • Provides protection for the cell • Allows cell to fill with water without bursting.(turgor pressure) • Found only in plant cells Cytoskeleton • Gives cell shape and plays a role in cell division. • Allows cellular organelles to move from place to place. Quiz Yourself If a cell’s job was to export lots of proteins, which organelles would it need more of than any of the others? If a cell needed to use lots of energy such as a muscle cell or a nerve cell (neuron), which organelle would it need lots of? Which organelle produced glucose(food) for a cell, and which type of cell is it found in? What is the only type of eukaryotic cell that will burst if filled with too much fluid and what organelle does it lack that causes this? The ribosome The rough ER The Golgi apparatus