* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
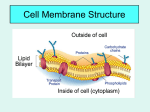
Cellular Transport In or Out? 1. What are some things that can pass through a window screen? 2. What are some things that can not pass through a window screen? Why is it important to keep these things from moving through the screen? 3. How is a window screen similar to a cell membrane? 4. Why is it important to regulate what moves into and out of the cell? The Cell Membrane Selectively permeable (semi-permeable) allows only certain substances to pass through cannot control the movement of water Cell membrane The Cell Membrane Double layer of lipids with proteins scattered throughout Protein Carbohydrate chain Lipid bilayer Hydrophilic head hydrophobic tail Protein The Cell Membrane The cell membrane helps to maintain homeostasis Homeostasis- maintaining a stable internal environment even though external conditions change Passive Transport No energy is required Diffusion, Osmosis, and facilitated diffusion are types of passive transport Diffusion Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Moves “down” or “with” the concentration gradient Does NOT require energy http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student _view0/chapter2/animation__how_ diffusion_works.html Diffusion Factors effecting the rate of diffusion 1. temperature (as temp increases rate increases) 2. pressure (as pressure increases rate increases) 3. steepness of the concentration gradient (the steeper the gradient the faster the diffusion) Osmosis Movement of WATER across a cell membrane Water always moves toward the higher concentration of solute particles Types of Solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Types of Solutions Isotonic – solutes inside = solutes outside Hypotonic – solutes are higher inside the cell water flows in, cell swells cell could burst if continues Hypertonic – solutes are higher outside the cell water leaves cell, cell shrinks Types of Solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Water particle Solute particle Hypertonic Types of Solutions Effects on Animal Cells http://www.nclar k.net/osmosisPo cus.gif The pictures below are red blood cells in different concentrations of salt solution. Identify which pictures are hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions. Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic Types of Solutions Effects on Plant Cells Which of these cells are in a hypotonic solution? Hypertonic solution? Hypotonic Hypertonic Onion cells plasmolysis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SooSsKkJo1o Types of Solutions Effects on Plant Cells Turgor pressurePlant cells fill with water and press against the cell walls making the cells rigid Types of Solutions Effects on Animal Cells Contractile Vacuolesstructure in protists that collects and expels excess water out of the cell to prevent the cell from exploding (lysing) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iG6D d3COug4 Facilitated diffusion Facilitated diffusion occurs when molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration with the aid of a protein molecule Does not require energy http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_v iew0/chapter2/animation__how_facili tated_diffusion_works.html Active Transport Requires energy moves from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration moves “up” or “against” the concentration gradient Active Transport LOW HIGH ENERGY FROM ATP PUSHES MOLECULES ACROSS THE MEMBRANE WATCH ACTIVE TRANSPORT LOW TO HIGH ENERGY NEEDED Active Transport http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animati on__how_the_sodium_potassium_pump_works.html Bulk Transport Sometimes the size of the particle or the amount that needs to be moved through the membrane is too large. Then bulk transport is used Bulk Transport Sometimes the size of the particle or the amount that needs to be moved through the membrane is too large. Then Bulk transport is used Bulk Transport Endocytosis- movement into a cell by forming a vacuole around the particles. Exocytosis- movement out of a cell by releasing the contents of a vacuole. Bulk Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Bulk Transport Pinocytosis- movement of large volumes of solution with dissolved solutes in or out of the cell Phagocytosis- movement of large particles into or out of the cell Bulk Transport An amoeba feeds on a Paramecium http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6rnhiMxtKU&fe ature=player_embedded Transport Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9wi PhcKlhTw