* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
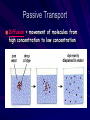
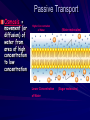
Cell Membrane Review Functions – Provides boundary for cell – Selectively Permeable: only allows certain things to pass through. “Picky” Ex: Window screen – Maintains homeostasis: balance within the cells Cell Membrane Structure vs. Function – Membrane is a phospholipid bilayer – Phospholipids: two sided molecule with a head that loves (hydrophilic) and a tail that repels (hydrophobic) water – Embedded Proteins: “club bouncers” Decide who goes in & out Markers for recognition TYPES OF TRANSPORT Passive Transport: -Uses No Energy -Movement from high concentration to low concentration Active Transport: – – Requires Energy (ATP) Usually against the concentration gradient (from low concentration to high concentration) Passive Transport Diffusion = movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration Passive Transport Osmosis = movement (or diffusion) of water from area of high concentration to low concentration Higher Concentration of Water Lower Concentration of Water (Water molecules) (Sugar molecules) HYPO/HYPER/ISO HYPOTONIC: •Concentration is lower outside cell than inside cell •HYPOTONIC means “below strength” •Water will move INTO cell causing it to SWELL •Cells could rupture if the cell takes in too much water •This increases pressure inside of cell (TURGOR PRESSURE) HYPERTONIC: •Concentration is higher outside the cell, lower inside cell •HYPERTONIC means “above strength” •H2O rushes OUT of cell causing it to shrivel •Can result in PLASMOLYSIS in plants which causes wilting ISOTONIC: Concentration outside the cell is the same as the inside of the cell ISO- means “equal to” or “same” Movement into cell = movement out of cell; cell does not change. Passive Transport Facilitated Diffusion = proteins are used to help larger molecules (like sugar) cross the membrane. Facilitated means “assisted”. Still passive. No energy required. Active Transport Movement against the concentration gradient. Molecules will move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and protein pumps Active Transport Endocytosis = the process by which cells take in particles; into the cell – Pinocytosis = drinking action, used for small particles or water – Phagocytosis = devouring action, used for large particles like food Exocytosis = the process by which cells remove wastes and large particles; exit the cell