* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
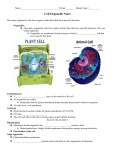
Plant Growth AKA “Cells” The Cell Membrane • The cell membrane or (plasma membrane) is a flexible boundary between the cell and its environment – It is the outermost structure making the outline of the cell The Cell Membrane • The cell membrane allows certain things in, such as water and nutrients, and other things out • This ability of the cell membrane to allow certain things in or out is referred to as selective permeability Cell Organelles The Nuts and Bolts of a Cell Centrioles Mitochondria Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Chromatin Nucleolus Cytoplasm Nuclear Membrane Cell Membrane Ribosome Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Vacuole Cell Organelles • Like many organisms have organs within them that have specific functions, cells have organelles • Organelles are membrane-bound structures within a eukaryotic cell that have specific functions The Cell Membrane • The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is a selectively permeable layer on the outside of the cell, which contains all of the organelles within. Cell Wall • A cell wall is a fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists which provides support and protection • The cell wall allows the cell to become quite turgid without bursting Mitochondria • A eukaryotic membrane-bound organelle that transforms energy stored in food molecules is called mitochondria – Mitochondria have highly folded membranes that produce energy-storing molecules • Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell Golgi Apparatus • The Golgi apparatus is an organelle in eukaryotic cells with a system of flattened tubular membranes • It sorts and packages proteins and sends them to their appropriate destinations Lysosome • A lysosome contains digestive enzymes and is responsible for digesting excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria Vacuole • A vacuole is a membrane-bound space in the cytoplasm of cells used for the temporary storage of materials – The vacuole in a plant is very large Centrioles • In animal cells, a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules called centrioles duplicate during interphase and move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase Chromatin • Long strands of DNA found in the eukaryotic cell nucleus is known as chromatin and condenses to form chromosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle in eukaryotic cells with a series of highly folded membranes surrounded in cytoplasm • It is the site of cellular chemical reactions – Can be rough “ER” with ribosomes attached or smooth ER without ribosomes Ribosomes • Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound organelles in the nucleus where proteins are assembled Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm is the clear, gelatinous fluid in cells that is the site of numerous chemical reactions – In eukaryotes, it suspends the organelles Nucleus • The nucleus is the central membrane-bound organelle that manages cellular functions and contains DNA • The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane which can dissolve or allow structures out to the cytoplasm Nucleolus • The nucleolus is found in the nucleus and produces ribosomes Review • To link to an Internet site on parts of the cell click here!