* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What type of cells did you observe?
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
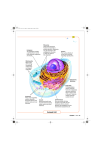
Aim: How can we describe the structure and function of cell organelles? AIM: How can we describe the structure and function of cell organelles? DN: What are organelles? Name at least two organelles and describe the function of each one. HW: Read pages 173-183, page 183 #1-6 ORGANIZATION CHART CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL PROKARYOTIC CELLS BACTERIA Prokaryotes All Bacteria They DO NOT have membrane bound organelles. They DO have: Cell Membranes Cell Walls DNA Ribosomes 2 Types of Eukaryotic Cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Both are complex, but there are differences What are those things inside the cell? Organelles- Specialized structures in cells that perform important cellular functions. Life Functions Nutrition – to get nutrients for energy Transport – to move materials from A to B Cell respiration – Energy: ATP Excretion – to get rid of metabolic waste Synthesis – to build, to make Regulation – to control Growth – to increase in size or number Reproduction – to make offspring CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTION: Protect the cell. Controls what comes in and out. CYTOPLASM FUNCTION: Protect and support the organelles within the cell. NUCLEUS Found in eukaryotic cells only! Function: Controls cell processes and contains the hereditary information - DNA ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM FUNCTION: Transport of materials 2 Types: Rough ER (has ribosomes) & Smooth ER RIBOSOMES FUNCTION: Protein Synthesi Cytoplasm or on Rough ER GOLGI APPARATUS FUNCTION: Packages Proteins MITOCHONDRIA FUNCTION: Powerhouse of the cell- cellular respiration Makes energy or ATP from food and oxygen. LYSOSOMES FUNCTION: Contain enzymes that can break down nutrients. Also they break down dead organelles. VACUOLES FUNCTION: Store materials such as water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates. MANY SMALL ONES IN ANIMAL CELLS, AND ONE BIG ONE IN PLANT CELLS. CENTRIOLES FUNCTION: • Involved in animal cell division • FOUND ONLY IN ANIMAL CELLS CHLOROPLASTS FUNCTION: Photosynthesis FOUND IN PLANT CELLS! CELL WALL Support FUNCTION: and protection for the cell and allows materials in and out of the cell. FOUND IN PLANT CELLS. CILIA & FLAGELLA FUNCTION: Made of protein and help with the movement of individual cells Animal cell Plant cell What do plant and animal cells have in common? AMIMAL CELL X X X X X X X X X PLANT CELL Cell Membrane X Cytoplasm X Nucleus X Endoplasmic Reticulum X Ribosome X Mitochondria X Lysosomes X Vacuole X Centriole Chloroplast X Cell Wall X Cheek Cell NUCLEUS Elodea Cell CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST