* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory and Structure
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
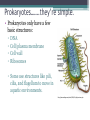
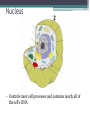
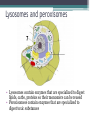
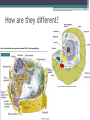
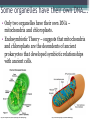
Cell Theory and Structure Discovery of the Cell • Scientists did not start using simple compound microscopes until the mid 1600’s. • Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at slices of cork. http://www.smithlifescience.com/cork2.GIF • Hooke named the ‘seemingly empty’ chambers ‘cells.’ • Around the same time, Anton von Leeuwenhoek was using a single-lens microscope to observe unicellular organisms in pond water for the first time. Cell Theory • Additional observations of cells in other living things led scientists to 3 basic conclusions, known as the cell theory. • Cell Theory states: ▫ All living things are composed of cells. ▫ Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. ▫ New cells are produced from existing cells. There are two categories of cells…… • Prokaryotes ▫ No nucleus ▫ Few organelles ▫ Small in size ▫ Ex: Bacteria Eukaryotes – Nucleus – Many organelles – Large in size – Ex: Humans, plants, fungi, etc. http://www.cod.edu/people/faculty/fancher/EukaryoticCell.jpg http://www.cod.edu/people/faculty/fancher/ProkaryoticCell.jpg Cell Structure • All cells, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, have DNA and a cell membrane. • Cells also contain organelles – specialized structures within the cell that perform certain tasks. • These organelles float around in the cell’s cytoplasm, which is mostly made of water. Prokaryotes…….they’re simple. • Prokaryotes only have a few basic structures: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ DNA Cell/plasma membrane Cell wall Ribosomes ▫ Some use structures like pili, cilia, and flagellum to move in aquatic environments. http://scienceblogs.com/clock/2006/11/cell_structure.php ….but they come in many varieties. http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.harlem-school.com/10TH/sci_pdf/graphics/prokaryotic_entities.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.harlemschool.com/10TH/sci_pdf/sci.html&h=396&w=284&sz=32&hl=en&start=12&tbnid=dQsSJBBu88uFiM:&tbnh=124&tbnw=89&prev=/images%3Fq%3Ddifferent%2Bshaped,%2Bprokaryotic%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa fe%3Dactive Eukaryotes are more complex. • Eukaryotes can be multicellular or unicellular. • Eukaryotes contain many organelles……. Do you know your Organelles? Cell (plasma) membrane • Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell. Nucleus • Controls most cell processes and contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA Ribosomes • assemble proteins. ▫ Some are free floating while others are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • There are two types: ▫ Rough – chemically modifies proteins that are produced by the ribosomes on its surface. ▫ Smooth – contains specialized enzymes and makes lipid components for the cell membrane. Golgi apparatus • Sorts, modifies, and/or packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage or secretion from the cell. Lysosomes and peroxisomes • Lysosomes contain enzymes that are specialized to digest lipids, carbs, proteins so their monomers can be reused • Peroxisomess contain enzymes that are specialized to digest toxic substances Cytoskeleton http://scienceblogs.com/clock/2006/11/cell_structure.php • A network of protein filaments (microtubules and microfilaments) that help the cell move and maintain its shape Mitochondria • Provides the cell with usable chemical energy ▫ It is the site of cellular respiration. How are they different? http://staff.tuhsd.k12.az.us/gfoster/standard/BCELL1_files/image005.jpg http://scienceblogs.com/clock/2006/11/cell_structure.php Plant cells have special features….. • Plants contain: ▫ Chloroplasts – create and store usable energy through the process of photosynthesis. ▫ Cell wall – provides the cell with rigid structure. ▫ 1 Large vacuole – used for the storage of water and some other materials Animal cells usually have many small vacuoles Some organelles have their own DNA…. • Only two organelles have their own DNA – mitochondria and chloroplasts. • Endosymbiotic Theory – suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts are the decendents of ancient prokaryotes that developed symbiotic relationships with ancient cells. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/chloroplasts/images/chloroplastsfigure1.jpg http://en.citizendium.org/images/c/c7/MitochondriaSMALL2.jpg