* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 Body Systems
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
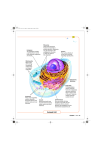
Chapter 3 Anatomy of Cells Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 1 Functional Anatomy of Cells The typical cell (Figure 3-1) Also called composite cell Varies in size; all are microscopic (Table 3-1) Varies in structure and function (Table 3-2) Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 2 Functional Anatomy of Cells Cell structures Plasma membrane—separates the cell from its surrounding environment Cytoplasm—thick gel-like substance inside of the cell composed of numerous organelles suspended in watery cytosol; each type of organelle is suited to perform particular functions (Figure 3-2) Nucleus—large membranous structure near the center of the cell Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 3 Cell Membranes Each cell contains a variety of membranes: Plasma membrane (Figure 3-3) Membranous organelles—sacs and canals made of the same material as the plasma membrane Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 4 Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model—theory explaining how cell membranes are constructed Molecules of the cell membrane are arranged in a sheet The mosaic of molecules is fluid; that is, the molecules are able to float around slowly This model illustrates that the molecules of the cell membrane form a continuous sheet Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 5 Cell Membranes Chemical attractions are the forces that hold membranes together Groupings of membrane molecules form rafts, each of which float as a unit in the membrane (Figure 3-4) Rafts may pinch inward, bringing material into the cell or organelle Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 6 Cell Membranes Primary structure of a cell membrane is a double layer of phospholipid molecules Heads are hydrophilic (water-loving) Tails are hydrophobic (water-fearing) Molecules arrange themselves in bilayers in water Cholesterol molecules are scattered among the phospholipids to allow the membrane to function properly at body temperature Most of the bilayer is hydrophobic; therefore water or water-soluble molecules do not pass through easily Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 7 Cell Membranes Membrane proteins (Table 3-4) A cell controls what moves through the membrane by means of membrane proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer Some membrane proteins have carbohydrates attached to them, forming glycoproteins that act as identification markers Some membrane proteins are receptors that react to specific chemicals, sometimes permitting a process called signal transduction Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 8 Cytoplasm and Organelles Cytoplasm—gel-like internal substance of cells that includes many organelles suspended in watery intracellular fluid called cytosol Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 9 Cytoplasm and Organelles Two major groups of organelles (Table 3-3): Membranous organelles are specialized sacs or canals made of cell membranes Nonmembranous organelles are made of microscopic filaments or other nonmembranous materials Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 10 Cytoplasm and Organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 3-5) Made of canals with membranous walls and flat, curving sacs arranged in parallel rows throughout the cytoplasm; extend from the plasma membrane to the nucleus Proteins move through the canals Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 11 Cytoplasm and Organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (cont.) Two types of endoplasmic reticulum: • Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes dot the outer surface of the membranous walls Ribosomes synthesize proteins, which move toward the Golgi apparatus and then eventually leave the cell Function in protein synthesis and intracellular transportation Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 12 Cytoplasm and Organelles Two types of endoplasmic reticulum (cont.) • Smooth endoplasmic reticulum No ribosomes border membranous wall Functions are less well established and probably more varied than for rough endoplasmic reticulum Synthesizes certain lipids and carbohydrates and creates membranes for use throughout cell Removes and stores Ca++ from cell’s interior. Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 13 Cytoplasm and Organelles Ribosomes (Figure 3-6) Many are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and many lie free, scattered through the cytoplasm Each ribosome is a nonmembranous structure made of two pieces, a large subunit and a small subunit; each subunit is composed of rRNA Ribosomes in the endoplasmic reticulum make proteins for “export” or to be embedded in the plasma membrane; free ribosomes make proteins for the cell’s domestic use Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 14 Cytoplasm and Organelles Golgi apparatus Membranous organelle consisting of cisternae stacked on one another and located near the nucleus (Figure 3-7) Processes protein molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 3-8) Processed proteins leave the final cisterna in a vesicle; contents may then be secreted to outside the cell Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 15 Cytoplasm and Organelles Lysosomes (Figure 3-9) Made of microscopic membranous sacs that have “pinched off” from Golgi apparatus The cell’s own digestive system; enzymes in lysosomes digest the protein structures of defective cell parts, including plasma membrane proteins, and particles that have become trapped in the cell Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 16 Cytoplasm and Organelles Proteasomes (Figure 3-10) Hollow, protein cylinders found throughout the cytoplasm Break down abnormal/misfolded proteins and normal proteins no longer needed by the cell Break down protein molecules one at a time by tagging each one with a chain of ubiquitin molecules and unfolding it as it enters the proteasome, then breaking apart peptide bonds Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 17 Cytoplasm and Organelles Peroxisomes Small membranous sacs containing enzymes that detoxify harmful substances that enter the cells Often seen in kidney and liver cells Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 18 Cytoplasm and Organelles Mitochondria (Figure 3-11) Made up of microscopic sacs; wall composed of inner and outer membranes separated by fluid; thousands of particles make up enzyme molecules attached to both membranes The “power plants” of cells; mitochondrial enzymes catalyze series of oxidation reactions that provide about 95% of cell’s energy supply Each mitochondrion has a DNA molecule, allowing it to produce its own enzymes and replicate copies of itself Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 19 Nucleus Definition—spherical body in center of cell; enclosed by an envelope with many pores Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 20 Nucleus Structure Consists of nuclear envelope (composed of two membranes each with essentially the same molecular structure as plasma membrane) surrounding nucleoplasm; nuclear envelope has holes called nuclear pores (Figure 3-12) Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 21 Nucleus Structure (cont.) Contains DNA (heredity molecules), which appear as the following: • Chromatin threads or granules in nondividing cells • Chromosomes in early stages of cell division • Functions of nucleus are functions of DNA molecules; DNA determines both structure and function of cells and heredity Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 22 Cytoskeleton The cell’s internal supporting framework made up of rigid, rodlike pieces that provide support and allow movement and mechanisms that can move the cell or its parts (Figure 3-13) Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 23 Cytoskeleton Cell fibers Intricately arranged fibers of varying lengths that form a three-dimensional, irregularly shaped lattice Fibers appear to support the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and “free” ribosomes Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 24 Cytoskeleton Cell fibers (cont.) Smallest cell fibers are microfilaments (Figure 3-14) • “Cellular muscles” • Made of thin, twisted strands of protein molecules that lie parallel to the long axis of the cell • Microfilaments can slide past each other, causing shortening of the cell Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 25 Cytoskeleton Cell fibers (cont.) Intermediate filaments are twisted protein strands slightly thicker than microfilaments; they form much of the supporting framework in many types of cells Microtubules are tiny, hollow tubes that are the thickest of the cell fibers; they are made of protein subunits arranged in a spiral fashion; their function is to move things around in the cell Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 26 Cytoskeleton Centrosome An area of the cytoplasm near the nucleus that coordinates the building and breaking of microtubules in the cell Nonmembranous structure also called the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) Plays an important role during cell division The general location of the centrosome is identified by the centrioles Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 27 Cytoskeleton Cell extensions Cytoskeleton forms projections that extend the plasma membrane outward to form tiny, fingerlike processes Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 28 Cytoskeleton There are three types of these processes; each has specific functions (Figure 3-15): • Microvilli—found in epithelial cells that line the intestines and other areas where absorption is important; they help to increase the surface area manyfold • Cilia and flagella—cell processes that have cylinders made of microtubules at their core; cilia are shorter and more numerous than flagella; flagella are found only on human sperm cells Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 29 Cell Connections Cells are held together by fibrous nets that surround groups of cells (e.g., muscle cells), or cells have direct connections to each other There are three types of direct cell connections (Figure 3-16) Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 30 Cell Connections Desmosome Fibers on the outer surface of each desmosome interlock with each other; anchored internally by intermediate filaments of the cytoskeleton Spot desmosomes, connecting adjacent membranes, are like “spot welds” at various points Belt desmosomes encircle the entire cell like a collar Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 31 Cell Connections Gap junctions—membrane channels of adjacent plasma membranes adhere to each other; have two effects: Form gaps or “tunnels” that join the cytoplasm of two cells Fuse two plasma membranes into a single structure Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 32 Cell Connections Tight junctions Occur in cells that are joined by “collars” of tightly fused material Molecules cannot permeate the cracks of tight junctions Occur in the lining of the intestines and other parts of the body, where it is important to control what gets through a sheet of cells Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. Slide 33