* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 3 Summary – page 179-187 Energy Transformers Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
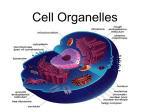
Today’s Objective: • To investigate and explain cellular processes, such as homeostasis, converting energy, the production of new materials, and transporting materials. Can be found in the book: Chapter 7.3 REMEMBER, cells have tiny organs inside them called organelles. Each organelle, just like the organs in your body, have a specific job they carry out for the cell’s survival. Also, REMEMBER some organelles have a membrane around them. What are they called? nucleus mitochondria While other organelles do not have a protective layer. ribosome Genetic Material The master set of directions for making proteins (making you) is contained in DNA. Prokaryotic cells only have one long strand of DNA Eukaryotic cells have different amounts of DNA (depending on what type of organism it is). Cell Control Center In prokaryotic cells, the DNA is found floating in the middle of the cell…. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found inside the nucleus. Cell Control Center Just as every team needs a leader, the cell needs a leader to give directions. Nucleus The nucleus is the leader of the eukaryotic cell because it contains directions to make proteins. Every part of the cell depends on proteins, so by containing the blueprints to make proteins, the nucleus controls the actions of all the organelles. Homeostasis Inside the cell Outside the cell Plasma membrane Plasma membrane • The plasma membrane (also called cell membrane) is a “skin” that covers the cell. • All cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) have a plasma membrane. Homeostasis Outside the cell Plasma Membrane Inside the cell • The plasma membrane maintains homeostasis (an internal balance) by controlling what goes in and out of the cell. Energy Transformers Cells have to transform energy in order to use it. There are two different organelles that do this as their job. CHLOROPLAST MITOCHONDRIA ● Has a membrane ● Has a membrane ● Only found in eukaryotic PLANT cells ● Found in ALL eukaryotic cells Chloroplasts: organelles that use light energy and transform it into food energy in eukaryotic PLANT cells. PHOTOSYNTHESIS CHLOROPLAST Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll Chlorophyll traps energy from sunlight and gives leaves and stems their green color. Chloroplast Chlorophyll Energy Transformers Mitochondria: membrane-bound organelles in ALL eukaryotic cells that transform food energy into chemical energy (that we use to perform all functions: walking, talking, thinking). Cellular respiration is the process by which mitochondria use food energy, and oxygen to create CO2 , water, and ATP (chemical energy) Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP Glucose Oxygen Gas Carbon Dioxide Water Energy It is the reverse process of photosynthesis