* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analytical Approaches in Cell Biology
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
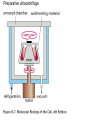
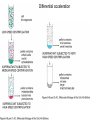
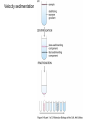
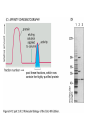
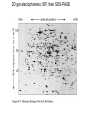
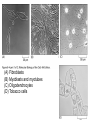
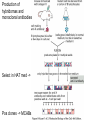
Analytical Approaches in Cell Biology BSCI 420 Sept 12, 2002 “Make everything as simple as possible, but not simpler” -Albert Einstein 1. Separation of cell components 2. Cell culture, fusion and hybridomas 1. Separatory techniques: Cells must first be disrupted by homogenization, osmotic rupture, detergent lysis, or ultrasonic disruption. A. Centrifugation is useful for separation on the basis of mass or density. [A8-7] preparative ultracentrifuge 1) Differential acceleration: Repeated centrifugation at progressively higher speeds, e.g. low 1000 X g med 20,000 X g high 80,000 X g very high 150,000 X g Preparative ultracentrifuge Differential acceleration Velocity sedimentation Equilibrium densitygradient centrifugation To sep. organelles or molecules of similar mass but diff. Densities. E.g., lysosomes & mitoch. Or labeled DNA from inlabeled. 2. Chromatography A) Ion exchange - Charged resin on beads, e.g. DEAE dextran (+) 0r phosphocellulose (-) charged. Oppositely charged molecules bind, released by salt solution. B) Gel filtration - Retards smaller molecules that enter pores in gel beads, so larger molecules come thru 1st. C) Affinity chromatography - Specific ligand or antibody bound to beads. Elute with buffer that dissociates ligand from protein, e.g. low pH, hi salt 3. Electrophoresis Separates based on migration rate in electrical field. Most common: SDS-PAGE Uniformly neg charged so migrate on the basis of size Isoelectric focusing; Run in solution of ampholines that maintain a pH gradient 2D gel electophoresis: IEF, then SDS-PAGE 2. Cell culture, Fusion , & Hybridomas 3 types of cell cultures: a) Primary cell cultures- Directly from an organism b) Normal cell lines - Cells that have been subcultured and adapted to cell culture (mortal-age and die) c) Transformed cell lines - Virus, mutated, or derived from a tumor. (immortal) All 3 can still retain some different cell f(x)s. (A) Fibroblasts (B) Myoblasts and myotubes (C) Oligodendrocytes (D) Tobacco cells Fusion, heterocaryons, and and hybrid cells Production of hybridomas and monoclonal antibodies Select in HAT med -> Pos clones -> MCABs