* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life is “Cellular”
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
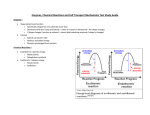
CHAPTER 7 CELLULAR STRUCTURE & TRANSPORT (P.168-193) Chapter 7, Section 1 (p. 169-173) Life is “Cellular” Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells Microscopes • Light microscopes – Visible light – Whole cells & larger organelles • Electron Microscopes – Electrons – Smaller cellular structures Prokaryotes Eukaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 7, Section 2 (p. 174-181) Animal Cell Plant Cell Nucleus • Contains DNA – Instructions for making proteins • Nucleolus – Ribosome assembly Nuclear Envelope • Controls what enters/exists the nucleus Cytoplasm • Jelly-like substance – Surrounds organelles • Functions – Movement of materials – Dissolved substances – Maintains structure Ribosome • Receives instructions from DNA – Synthesizes proteins for the cell • “Free” – Proteins stay in cell • “Attached” – Proteins shipped to another organelle or out of cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) • Contains ribosomes • Chemically modifies newly made proteins Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) • No ribosomes • Breaks down toxic chemicals • Synthesis of membrane lipids & steroids Golgi Apparatus • Sorts and packages proteins to send to another organelle or for export out of the cell Lysosome • Contains enzymes – Break down of large molecules Mitochondrion • Converts energy stored in food molecules into energy cell can use – ATP Cytoskeleton • Made up of – Microtubules – Microfilaments • Function – Structural support – Helps move substances inside of the cell Centrioles • Coordinates cell division • Organizes cytoskeleton • ONLY found in animal cells Central Vacuole • Storage – Water, toxins, sugars • Provides internal support to plant cell by creating “turgor pressure” Chloroplast • Site of photosynthesis – Converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose • ONLY in plant cells Cell Membrane • Controls what enters and exits the cell Cell Wall • Surrounds the cell membrane • ONLY in plant cells – Structural support – Made of cellulose Chapter 7, Section 3 (p.182-189) CELL BOUNDARIES Phospholipid Fluid Mosaic Model • Phospholipid bilayer gives the membrane structure and fluidity Diffusion • Movement of substances across a membrane toward a state of equilibrium – High Low Concentration – NO membrane protein required – NO energy required Diffusion of Gasses Osmosis • Diffusion of water across a membrane – High low water potential – No membrane protein – No energy required • Plant cells are less sensitive because of their cell wall Osmosis in Grapes • Predictions: • Observations: Osmosis in Grapes • Explanation: Facilitated Diffusion • Transport of substances that are large or polar/charged across a membrane – High Low Concentration – Membrane protein required – NO energy required Active Transport • Movement of molecules across a membrane against the concentration gradient – Low High Concentration – Membrane protein required – Energy required Bulk Transport Exocytosis • Release of material from the cell Endocytosis • Taking in of materials into cell – Vesicle fuses with cell membrane – Vesicle formed by cell membrane Low High OR High Low ENERGY REQUIRED!