* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chloroplasts Cell Wall
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
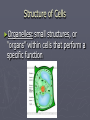
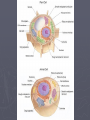
Cell Structure & Function Cells ► All living things on Earth are made of cells. ► Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in living things. ► Living cells come only from other living cells. ► Cells are so tiny you could fit more than a million of them on a period at the end of a sentence. ► You cannot see cells without a microscope. Cells ► Cells were named by Robert Hooke. ► 1st scientist to call spaces in cork cells he observed under the microscope “cells.” ► Comes from the Latin word cella which means “little rooms”. ► Unicellular: one cell – bacteria. ► Multicellular: many cells –humans have over 200 different types of cells (blood, bone, skin) and an estimated 100 trillion total cells. How Cells Function ► Each can take in nutrients, convert these nutrients into energy, carry out specialized jobs, and reproduce as necessary. How Cells Work ►Each cell stores its own set of instructions for carrying out each of these activities. Structure of Cells ►Organelles: small structures, or “organs” within cells that perform a specific function What’s In a Cell? ► Read the passage. ► As you answer the question, HIGHLIGHT the part of the passage that gives evidence for your answer. ► Bullet form answers are okay, but should be detailed. Functions of Organelles ► Each organelle has a job to do to help the cell function properly. ► Read about each of the organelles that follow. Organelles in Cells ► There are many organelles in each cell. ► Plant cells have two extra organelles that animal cells do not have. Animal Cells: Cell Membrane ► Cytoplasm ► Nucleus ► Nuclear Membrane ► Ribosomes ► Endoplasmic Reticulum ► Golgi Bodies ► Mitochondria ► Lysosomes ► Plant Cells: ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Mitochondria Lysosomes Chloroplasts Cell Wall Cell Membrane ► Outer structure that surrounds the cell ► Supports & protects the cell ► Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell ► Barrier between cell and its environment Cytoplasm ► Cell’s environment or inner space ► Made of mostly water ► Contains the organelles ► Site of most cell activity Nucleus ► The cell’s computer or brain ► Controls the cell activities ► Contains all the information the cell needs to do specific jobs, grow, and divide ► Information is stored in DNA molecules ► Contains the nucleolus which makes ribosomes ► Determines what proteins will be made Nuclear Membrane ► Protects and guards the nucleus ► Controls movement of materials in and out of the nucleus ► Keeps the DNA inside the nucleus ► Allows other materials to pass in and out of the nucleus Ribosomes ► Makes the proteins the cell needs to survive and grow ► Produces the Protein which is the Product of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) ► The transportation system of the cell ► Carries material through cell ► Allows reactions to happen in the cell ► Where the ribosomes do their work ► Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it so the proteins they make can be released directly into the ER for transport ► Smooth ER collects things and contains them Golgi Bodies ► Packs & carries the proteins ► Prepares the proteins for use or delivery outside the cell Mitochondria ► Cell’s powerhouse or power generator ► Supplies the energy ► Breaks down sugar molecules into energy ► Need oxygen to make energy and give off carbon dioxide as waste Lysosomes ► Cell’s recyclers ► Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules ► Contains enzymes which break down the proteins ► Digests old cell parts Chloroplasts ► Plant cells only ► Power generator for the plant ► Give plants their green color ► Uses energy from the sun to make food for the plant through photosynthesis Cell Wall ► Plant cells only ► Made of cellulose ► Surrounds the cell membrane ► Gives plants their shape, structure, and protection ► Allows H2O, O2, and CO2, to pass in and out of the cell Can you remember the function of each? Cut out the symbols and glue them next to the correct cell part. B. A. Cell = City G. C. H. D. I. E. F. J.