* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 8: Organelles and what they do
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
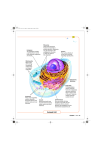
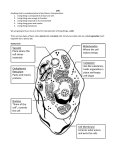
Happy Wednesday Buffs! Bellwork: Name at least two things Prokayotes and Eukaryotes have in common and at least two things that make them different. Projects… Are due one week from today. After today you should have a good idea about what you want to do and should be making plans to get started. There are many theories about how the first Eukaryotes emerged. The Endosymbiotic Theory is the most widely accepted The Endosymbiotic Theory states that the organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled prokaryotes. Break it down…. Endo = inside Symbiosis = a beneficial relationship Fat Tony: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bBjD4A7R2xU Endo. Theory with Playdoh: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EgaGh9-mFnQ Explains how organelles were most likely formed Also explains why organelles are membrane-bound Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryo tic Cell #1 Prokaryotic Cell #2 (chloroplast) NEW Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryoti c Cell #1 Prokaryotic Cell #2 (mitochondria) NEW Eukaryotic Cell Homework... color the cells A B C D E F G H I J Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Mitochondria Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Ribosomes Vacuoles Cell Walls Flagella CUT it Up!! Foldable time…. Follow my Instructions Cell Organelles and their Functions Page 11: Essential question: What are the organelles in a cell and what do they do? Cells Cells are the basic unit of all living things. IF IT IS ALIVE, IT HAS CELLS! Cell Theory: All organisms are made up of one or more cells The cell is the basic unit of all organisms all cells come from cells Two Types of Cells A B C D E F G H I J Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Mitochondria Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Ribosomes Vacuoles Cell Walls Flagella A. Cell Membrane: holds the cell together and allows nutrients into the cell. A B. Cytoplasm the It watery gel inside a cell. holds the ORGANelles. B C. Mitochondria ORGANelle that produces energy for the cell. C D. Nucleus The nucleus controls the cell. It contains the cell’s DNA. D E. Endoplasmic Reticulum A network of membranes throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. It helps to move materials around the cell Can be smooth or rough. E F. Golgi apparatus Responsible for sorting, packaging, and shipping the proteins produced in the ER. F G. Ribosomes help in the synthesis of proteins. Some ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. G H. Vacuoles Vacuoles are spaces in the cytoplasm where food and chemicals are stored H I. Cell Wall Cell Walls are in plant cells and bacteria They I make the cell strong and rigid J. Flagella Can be found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells J Used for movement

































![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-150x150.png)