* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL MEMBRANE PLASMA MEMBRANE
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
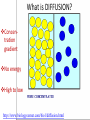
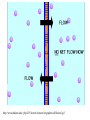
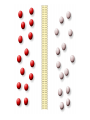
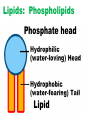
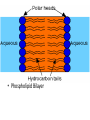
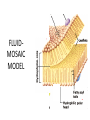
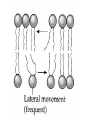
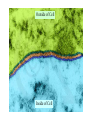
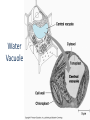
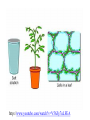
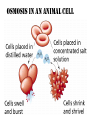
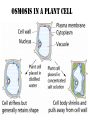
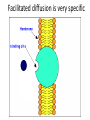
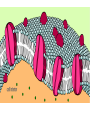
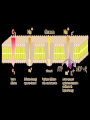
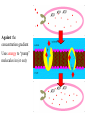
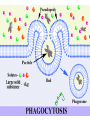
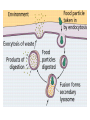
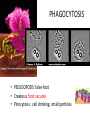
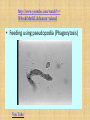
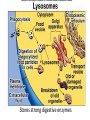
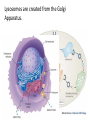
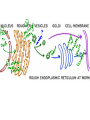
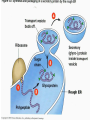
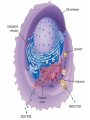
MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF A CELL CELL MEMBRANE PLASMA MEMBRANE TYPES OF TRANSPORT Active Transport • “HIGH ENERGY” Passive Transport • Energy (ATP) Required • “LAZY” • Controlled by the cell • No energy (ATP) required • Controlled by the movement of molecules What is DIFFUSION? Concentration gradient No energy High to low http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/diffusion.html Until Equilibrium Is reached http://www.indiana.edu/~phys215/lecture/lecnotes/lecgraphics/diffusion2.gif What is OSMOSIS? http://ntri.tamuk.eNot Lots du/class/ryan/passof Water Here ive.html • Diffusion of water • Water moves from high to low http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/lectures/osmosis.htm WATER Lots of Water Here What is the function of membrane? • Homeostasis • Controls movement of materials in and out of cell Do you remember what organic molecule the membrane is made of? Lipids: Phospholipids Phosphate head Lipid • Phospholipid Bilayer FLUIDMOSAIC MODEL Outside of Cell Inside of Cell PASSABLE • Monomers: amino acids, glucose, glycerol, F.A. • H2O, CO2, O2, NON-PASSABLE • Polymers: starch, proteins, triglycerides • charged ions (Na+, Cl-) What happens when a cell is placed in a solution with the same concentration as inside the cell? ISOTONIC SOLUTION •The cells stay the same size Normal Red Blood Cells What happens when an animal cell is placed in pure water? HYPOTONIC SOLUTION Swollen Red Blood Cells •The cells swell What happens to plants in a hypotonic solution? Plant cell placed in pure water? •Will not rupture due to cell wall •Turgor Pressure Video Water Vacuole Contractile Vacuoles What happens to an animal cell placed in salt water? HYPERTONIC SOLULTION Shriveled Red Blood Cells •The cells shrivel up Plants in a hypertonic Solution Plant cell placed in salt water? •Cytoplasm and membrane shrivel up •Cell wall remains in place •Plasmolysis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V56Zy7uLFEA Osmosis in an animal Cell Osmosis in a Plant Cell Facilitated Diffusion • Faster with help of a protein • No chemical reaction • NO ENERGY needed! • Examples: enzymes and glucose Facilitated diffusion is very specific ACTIVE TRANSPORT What if you need to get molecules to go against diffusion? Against the concentration gradient Uses energy to “pump” molecules in (or out) What if the food is too big to fit through the cell membrane? 2 TYPES ENDOCYTOSIS PHAGOCYTOSIS • PSEUDOPODS: false-foot • Creates a food vacuole • Pinocytosis: cell drinking, small particles http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= W6rnhiMxtKU&feature=related • Feeding using pseudopodia (Phagocytosis) You Tube What is needed to digest another cell after it is eaten? Stores strong digestive enzymes Lysosomes are created from the Golgi Apparatus. Golgi Body http://www.sumanasinc.com/webco ntent/animations/content/vesiclebu dding.html What must a cell do with undigested waste? EXOCYTOSIS • Cell egestion • Removal of undigested food • Vacuole moves to edge of cytoplasm and opens up • Opposite of endocytosis • Exocytosis